This is a default text for your page TEM1 Class Antibiotic Resistance Proteins. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Structural highlights
1xpb is a 1 chain structure with sequence from Escherichia coli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
|
| Ligands: | |
| Activity: | Beta-lactamase, with EC number 3.5.2.6 |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum |
| Related: | 1axb, 1bt5, 1btl, 1ck3, 1erm, 1ero, 1erq, 1esu, 1fqg, 1jtd, 1jtg, 1jvj, 1jwp, 1jwv, 1jwz, 1lhy, 1li0, 1li9, 1m40, 1nxy, 1ny0, 1nym, 1nyy, 1pzo, 1pzp, 1s0w, 1tem, 1xxm, 1yt4, 1zg4, 1zg6, 2v1z |
Background and History
Antibiotics have long been the primary line of defense against many infections. The advent of penicillin in the 1930s brought an end to an era of uncertainty: diseases once considered fatal became treatable. Unfortunately, natural selection stops for no species. Resistance to some form of antibiotic now has become standard for many infections.[A] Moreover, their liberal usage have resulted in “superbugs”, which are resistant to multiple antibiotics.[B] These strains are capable of secreting enzymes capable of deactivating the antibiotic or modifying their cell walls to render the antibiotic ineffective.
Many antibiotics such as penicillin, their derivatives (penams), and cephalosporins (cephams) possess a β-lactam ring (Figure 1).
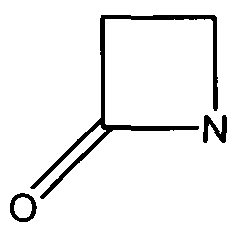
Figure 1. The beta-lactam ring is highlighted in red. Beta-lactamases function in hydrolyzing the amide bond within the ring, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. (Image Credit: Wikipedia)
β-Lactamases function by hydrolyzing the β-lactam ring within the antibiotic (Figure 2). This prevents the interaction between the cell wall and the antibiotic.
Figure 2. Bacteria are capable of becoming antibiotic resistant by catalyzing the hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring.
The TEM-1 subclass is one of the most common of all β-Lactamases.[3] Their prevalence began when bacteria started exhibiting penicillin resistance on a mass scale. Since the TEM-1 subclass has been prevalent for many years, many inhibitors have either been discovered or synthesized to prevent their catalytic function.
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.


