Sandbox Reserved 1181
From Proteopedia
|
Old Stuff:
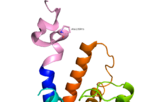
Fig. 1: A135P Mutation and effect on stalk stability [1].
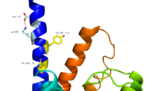
Fig. 2: Stalk stabilized by salt bridge between Glu133-Lys136. Residues in yellow are demonstrated to have an effect on ligand binding affinity.[1]
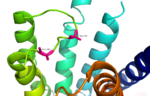
Fig. 3: Active sites linked to glucagon binding affinity located on ECL1 are labeled[1].
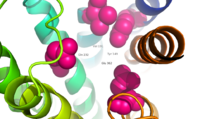
Fig. 9: Location of anchoring pocket within central cavity.[1]




