Insulin is a very important endocrine protein. Indeed, it is the only hypoglycemic hormone of the human body. This protein is secreted in the beta cells of the Langerhans’ islet in the pancreas and takes part in the glycogenesis. This molecule helps the transportation of glucose into the cells, thus reducing the blood sugar rate, contrary to glucagon.
Insulin also has a huge effect on growth and thereby has a lot of structural similarities with its main associated growth factor: IGF-1. Both share lots of properties thanks to their 60% similarity.
IGF-1 is a peptidic hormone of 69 amino acids which is secreted by the liver.
This protein deals with a large scale of regulations, from growth to nutrition and it is even implied in stress response, breeding and longevity.[1].
It is the main actor in primary growth cell control.
History
Biological structures and interactions
Structures
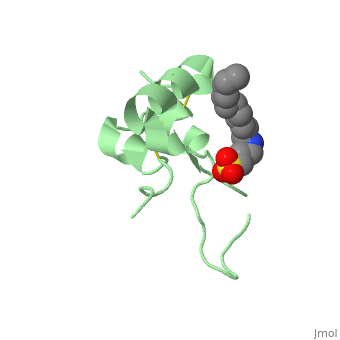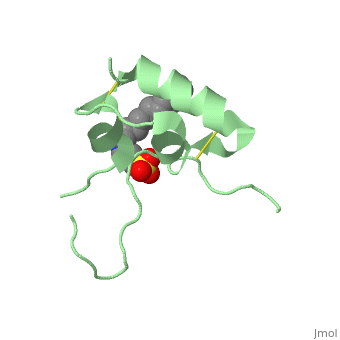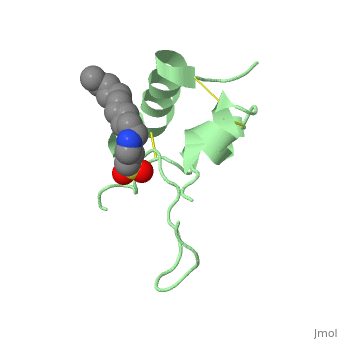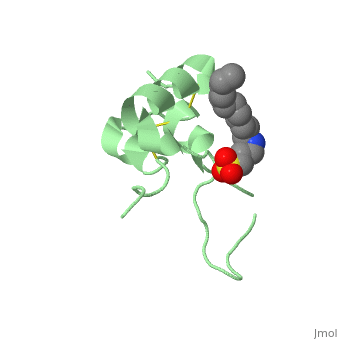
IGF-1 is a 8.28 kDa protein consisting of 69 amino acids.
The coding RNA of this protein creates 4 isoforms differing from each other due to RNA splicing.
Nevertheless, all 4 of them have cysteine residues that are able to make disulfide bond. This enable them to link to IGF-1 receptor.
It’s secondary structure as shown here is composed of alpha helix and beta strand.
Stimulating interaction : IGF1 - IGF1R
Inhibiting interaction : IGF1 - IGFBP
Metabolism
Biological context
Related diseases
Mutations,...
Applications