Sandbox Reserved 1269
From Proteopedia
|
Contents |
Function of 1YSA
1YSA is a transcription factor that activates over 30 genes necessary for amino acid or biosynthesis. 1YSA binds to the DNA sequence: 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3' (1).
Structure, Interactions, and Location
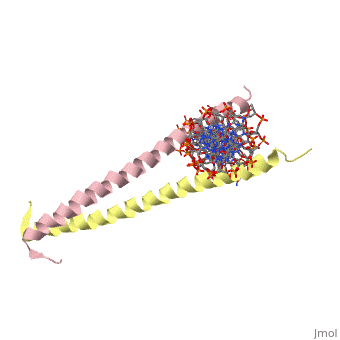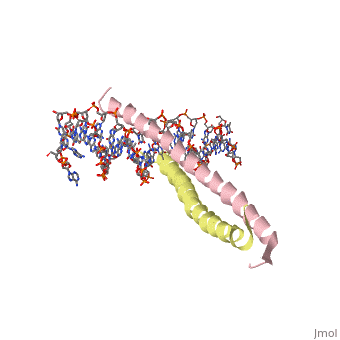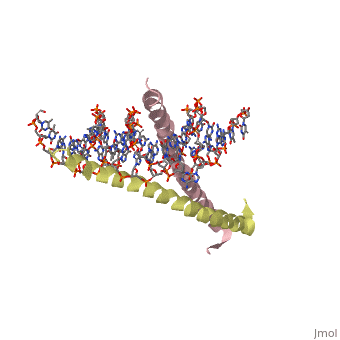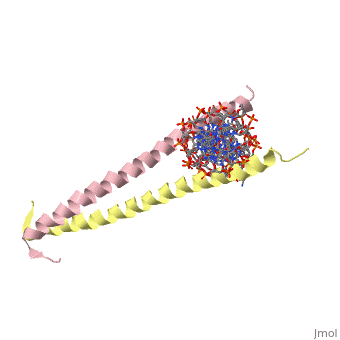
1YSA is a . There are both polar and regions within 1YSA. It interacts with DNA and binds DNA as a dimer. 1YSA interacts in several locations within the DNA. Additionally, 1YSA interacts with the protein Gcn4. Within DNA, 1YSA binds to DNA (5'-3 D(*tp*tp*cp*cp*tp*ap*tp*gp*ap*cp*tp*cp*ap*tp*cp*cp*a4 P*gp*tp*t)-3') and DNA (5'-9 D(*ap*ap*ap*cp*tp*gp*gp*ap*tp*gp*ap*gp*tp*cp*ap*tp*a10 P*gp*gp*a)-3') (2). The location of 1YSA within a cell is in nucleus P03069 (3).
Origin
1YSA originates from the organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae, or commonly known as baker's yeast (4).
References
(1) www.proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1ysa
(2) www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=1ysa
(3) www.pdbj.org/mine/summary/1ysa
(4) www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P03069