From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 02/09/2015, through 05/31/2016 for use in the course "CH462: Biochemistry 2" taught by Geoffrey C. Hoops at the Butler University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1051 through Sandbox Reserved 1080.
|
To get started:
- Click the edit this page tab at the top. Save the page after each step, then edit it again.
- Click the 3D button (when editing, above the wikitext box) to insert Jmol.
- show the Scene authoring tools, create a molecular scene, and save it. Copy the green link into the page.
- Add a description of your scene. Use the buttons above the wikitext box for bold, italics, links, headlines, etc.
More help: Help:Editing
|
DgcZ from E. coli
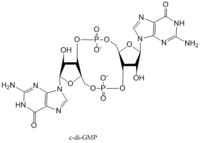
Diguanylate cyclases synthesize cyclic dimeric-GMP (c-di-GMP) from two GTP molecules.
C-di-GMP is a second messenger in the production of poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine (poly-GlcNAc)
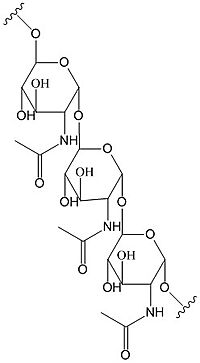
poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine
, a polysaccharide required for
E. coli biofilm production. This biofilm allows
E. coli to adhere to extracellular surfaces. The DgcZ protein is made of two domains: the catalytic GGDEF domain responsible for sythnesizing c-di-GMP and the regulatory CZB domain that binds zinc. When zinc is bound, the CZB and GGDEF domains adopt conformations that inhibit DgcZ function.
Structural Overview
GGDEF Domain
CZB Domain
Mechanism of Action
Zinc Ligand(s)
Other Ligands
References