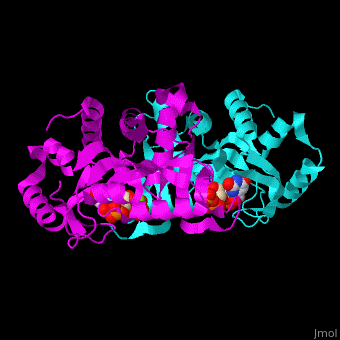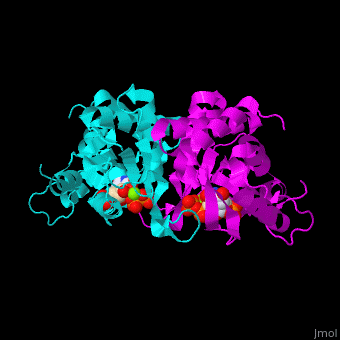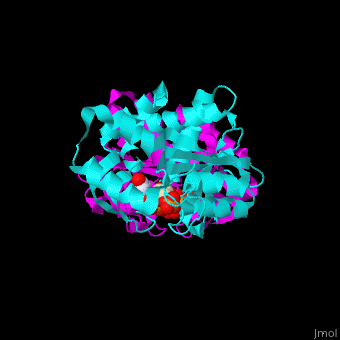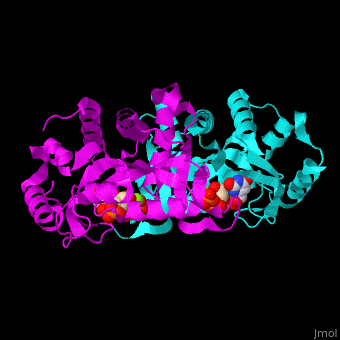Function
Phosphoribosyltransferase (PRT) are transferases which belong to several classes:
1. Hypoxanthine-guanine PRT (HPRT). HPRT is part of the purine biosynthesis and catalyzes the formation of GMP from guanine, xanthosine monophosphate from xanthosine and of IMP from hypoxanthine and 5-phospho-a-D-ribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP)[1].
2. Orotate PRT (OPRT). OPRT is part of the pyrimidine biosynthesis and catalyzes the formation of orotidine 5’-monophosphate (OMP) from orotate and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP)[2].
3. Quinolinic acid PRT (QAPRT ). QAPRT is a degrading enzyme found in the brain[3].
4. Uracil PRT (UPRT). UPRT catalyzes the formation of UMP from uracil and PRPP. Adenine PRT (APRT). APRT catalyzes the formation of AMP from adenine and PRPP[4].
5. Nicotinate nucleotide dimethylbenzimidazole PRT (NN:DBI PRT). NN:DBI PRT is part of riboflavin, porphyrin and chlorophyll biosynthesis[5].
6. Anthranilate PRT (ANPRT). ANPRT participates in phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis and catalyzes the formation of anthraniline from phosphoribosyl anthranilate[6].
7. ATP PRT participates in histidine biosynthesis and catalyzes the formation of ATP from phosphoribosyl ATP and diphosphate[7]. See ATP Phosphoribosyl Transferase.
8. Nicotinate PRT (NIPRT). NIPRT catalyzes the formation of nicotinate from nicotinate ribonucleotide and diphosphate[8].
9. Nicotinamide PRT (NMPRT). NMPRT catalyzes the formation of nicotinamide from nicotinamide ribonucleotide (NMN) and diphosphate[9].
Disease
Mutations in HPRT are involved in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome and hereditary gout[10].
Relevance
NMPRT inhibition is a target in controlling inflammation disorders[11].
Structural highlights
The structure of the yeast OPRT contains the two reaction products: and [12]. .