Sandbox RDE-1
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Introduction
|
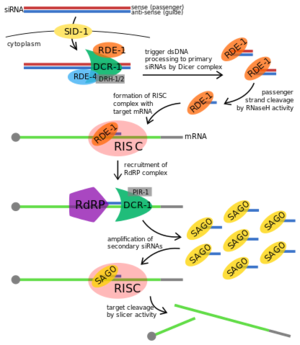
The rde-1 gene locus was first characterized in C. elegans mutants resistant to RNAi, and is a member of a highly conserved Piwi gene family that includes plant, Drosophila, and vertebrate homologs. RDE-1 (RNAi-DEfective 1) is a primary Argonaute protein required for RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Structure
Canonical Argonaute proteins possess three primary domains forming a crescent-shaped base: the PAZ, MID, and PIWI domains. PAZ and MID orient and anchor the double-stranded siRNA by binding to the 3’ and 5’ termini, respectively, leaving the internal nucleotides accessible for base pairing. The PIWI domain folds into an RNase H-like structure, and contains the conserved catalytic triad “DDH” (two aspartate residues, one histidine residue). The crystal structure of RDE-1 has not been formally elucidated, but can be assumed to closely resemble its human homologs. RDE-1 protein consists of 1020 amino acids. [1]
Importance/Function
Disease
Relevance
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
