Main Page
From Proteopedia
|
ISSN 2310-6301
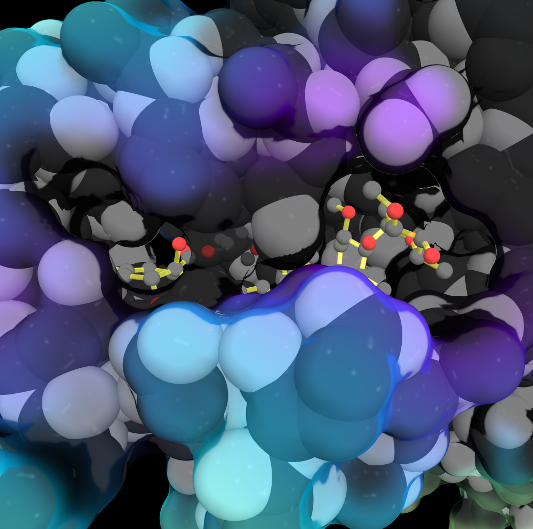
Because life has more than 2D, Proteopedia helps to understand relationships between structure and function. Proteopedia is a free, collaborative 3D-encyclopedia of proteins & other molecules.
| |||||||||||
| Selected Pages | Art on Science | Journals | Education | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
How to add content to Proteopedia Who knows ... |
Teaching Strategies Using Proteopedia |
||||||||||
| |||||||||||