Function
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (Pdk1) activates many other kinases. Pdk1 main effector is protein kinase B (Akt). . Pdk1 is important in signaling pathways activated by growth factors and hormones. It interacts with membrane phospholipids. [1]
Disease
Inhibition of Pdk1 leads to increase in α-secretase activity at the neuronal surface causing cellular prion protein and amyloid precursor protein to be cleaved into their nonpathogenic forms.
Structural highlights
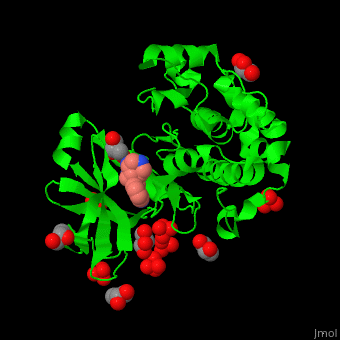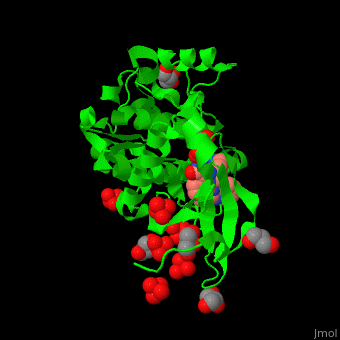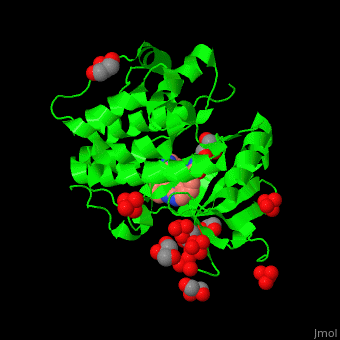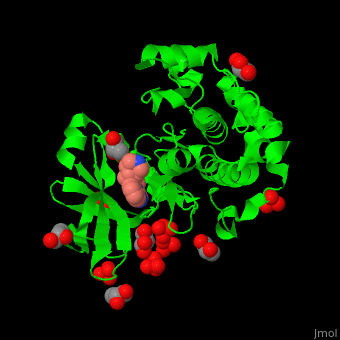
Pdk1 structure contains 2 domains: kinase (residues 71-359 in human) and PH (residues 459-550) in human). The PH (Plecksin Homology) domain interacts with phospholipids. The kinase domain (kd) contains 3 binding sites. These are for substrate-binding, ATP-binding and allosteric activator docking (PIF - [Pdk1-Interacting Fragment] -pocket). . Water molecules shown as red spheres.