Copper is one of the most important metallic cofactor involved in enzyme catalysed reactions. In living organisms, its function is related to the redox properties of copper. However it is toxic at all concentration, therefore it needs to be strictly controlled by molecular mechanisms.[1]
Function
Multicopper oxidases are enzymes involved in copper homeostasis. Indeed, free copper present in a cell (so, not bounded to a protein) is harmful and can cause cellular damage. It needs to be regulated.
Multicopper oxidase acts probably for the detoxification of copper present in the periplasmic space. It oxidizes the Cu+ into Cu2+ and prevents its uptake by the cytoplasm. It also possesses a phenoloxidase and a ferroxidase activity which can be involved in the prevention of oxidative damage.[2]
Multicopper oxidase might also be involved in the regulation of metal transport.
Multicopper oxidases are able to oxidise their substrates thanks to their particular structure. They own four copper ions (Cu1001, Cu1002, Cu1003 and C1004) dispatched between two important areas : the mononuclear copper center (Cu1001) and the trinuclear copper center (Cu1002, Cu1003 and Cu1004).
They accept an electron in the and transfer it to the trinuclear copper center which binds to a molecule of dioxygen. The dioxygen receives four electrons from this transfer. It is transformed into two molecules of water.[3] Three differents copper centres exist that can be differentiated spectroscopically: Type 1 or blue ()(Cu1001), type 2 or normal (Cu1004) and type 3 or coupled binuclear (Cu1002 and Cu1003).[4][5]
Mechanism
Multicopper oxidase catalyze the oxidation of different substrates by reducing O2 into H2O without releasing activated oxygen species (H2O2).
Multicopper oxidase contain 3 types of copper ions involved in the transfer of electrons from the substrate to the dioxygen. The first type of copper, type 1, (Cu1001) mediate the electron transfer from the substrate to the other coppers. The three other copper are called the trinuclear copper center. It is the key element for the oxygen reduction. It contains a type 2 copper (Cu1002) and 2 type 3 copper ions, binuclear ions, (Cu1003 and Cu1004). The final electron acceptor, O2, is bound to this last type of copper and is reduced into two molecules of water.[6]
Disease
If the amino acids 500 and 501 are mutated from CH to SR, the residual activity and loss of resistance to copper. E. Coli die.
Structural highlights
Multicopper Oxidase CueO 4e9s is a protein containing one chain with sequence from Ecoli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
|
| Ligands: | 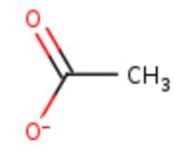 Figure 1: Acetate ion. [7] |
| Related: | 4e9p, 4e9q, 4e9r, 4e9t |
| Gene: | cueO, yacK, b0123, JW0119 (ECOLI) |
| Function: | binding of a metal ion |
| Process: | oxidation-reduction |
| Position: | bound at the outer membrane in the periplasmic space |
| Chain: | A |
| Sequence domain: | Cupredoxin, Multicopper oxidase type 1, type 2, type 3 and a copper-binding site |
| Number of amino acids: | 489 |
| Production and extraction: | Escherichia Coli |
| Initial gene: | sequence from amino acid 29 to amino acid 516 from P36649 |
| Specific region: | contain a methionine rich region (aa355 to aa400) that can be important for copper tolerance in bacteria |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, ProSAT, EMBL-EBI |
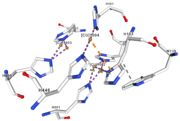
In the chain, 5 ligands are present: an acetate ion (C2H3O2) and 4 copper ions.
|
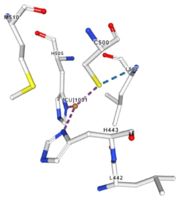
| Cu1001: The copper ion is bound thanks to 3 metal protein interactions with H443, H505 and C500, structure stabilised by L502, M510 by hydrogen bonds |
| Cu1002: 2 atoms of Cu, bonds twice by metal interaction (2x3) with 3 histidine : H501, H103, H141 stabilised by hydrophobic contact with W139 |
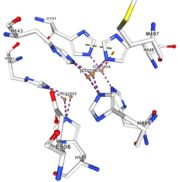 Figure 4: Copper 1003 [10] | Cu1003: 2 CU bond with 3histidine : H499, H143, H448 by 2 metal interactions. h448 is stabilised by Pi interactions with [CU]1004 and H101 |
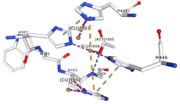 Figure 5: Copper 1004 [11] | Cu1004: one single atome of CU bonds once by metal interactions with 2 H ( and one ACT[1005]) : H101 and H446 stabilised by Pi interactions with H103 and H448. [CU]1004 has Pi interactions with H103 and H448. H113 and H446 Pi interactions |
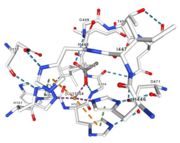 Figure 6: Acetate ion 1005 [12] | ACT[1005]: is linked by hydrogen bonds to G104 and G449 |
Cu1002, Cu1003, Cu1004 and ACT[1005] are near in the space, the 3 CU form a triangle.
The amino acid sequence is:
|
| 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 |
| A | E | R | P | T | L | P | I | P | D | L | L | T | T | D | A | R | N | R | I | Q | L | T | I | G | A | G | Q | S | T |
| 59 | 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 |
| F | G | G | K | T | A | T | T | W | G | Y | N | G | N | L | L | G | P | A | V | K | L | Q | R | G | K | A | V | T | V |
| 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 | 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 | 111 | 112 | 113 | 114 | 115 | 116 | 117 | 118 |
| D | I | Y | N | Q | L | T | E | E | T | T | L | H | W | H | G | L | E | V | P | G | E | V | D | G | G | P | Q | G | I |
| 119 | 120 | 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | 125 | 126 | 127 | 128 | 129 | 130 | 131 | 132 | 133 | 134 | 135 | 136 | 137 | 138 | 139 | 140 | 141 | 142 | 143 | 144 | 145 | 146 | 147 | 148 |
| I | P | P | G | G | K | R | S | V | T | L | N | V | D | Q | P | A | A | T | C | W | F | H | P | H | Q | H | G | K | T |
| 149 | 150 | 151 | 152 | 153 | 154 | 155 | 156 | 157 | 158 | 159 | 160 | 161 | 162 | 163 | 164 | 165 | 166 | 167 | 168 | 169 | 170 | 171 | 172 | 173 | 174 | 175 | 176 | 177 | 178 |
| G | R | Q | V | A | M | G | L | A | G | L | V | V | I | E | D | D | E | I | L | K | L | M | L | P | K | Q | W | G | I |
| 179 | 180 | 181 | 182 | 183 | 184 | 185 | 186 | 187 | 188 | 189 | 190 | 191 | 192 | 193 | 194 | 195 | 196 | 197 | 198 | 199 | 200 | 201 | 202 | 203 | 204 | 205 | 206 | 207 | 208 |
| D | D | V | P | V | I | V | Q | D | K | K | F | S | A | D | G | Q | I | D | Y | Q | L | D | V | M | T | A | A | V | G |
| 209 | 210 | 211 | 212 | 213 | 214 | 215 | 216 | 217 | 218 | 219 | 220 | 221 | 222 | 223 | 224 | 225 | 226 | 227 | 228 | 229 | 230 | 231 | 232 | 233 | 234 | 235 | 236 | 237 | 238 |
| W | F | G | D | T | L | L | T | N | G | A | I | Y | P | Q | H | A | A | P | R | G | W | L | R | L | R | L | L | N | G |
| 239 | 240 | 241 | 242 | 243 | 244 | 245 | 246 | 247 | 248 | 249 | 250 | 251 | 252 | 253 | 254 | 255 | 256 | 257 | 258 | 259 | 260 | 261 | 262 | 263 | 264 | 265 | 266 | 267 | 268 |
|
| C | N | A | R | S | L | N | F | A | T | S | D | N | R | P | L | Y | V | I | A | S | D | G | G | L | L | P | E | P | V |
| 269 | 270 | 271 | 272 | 273 | 274 | 275 | 276 | 277 | 278 | 279 | 280 | 281 | 282 | 283 | 284 | 285 | 286 | 287 | 288 | 289 | 290 | 291 | 292 | 293 | 294 | 295 | 296 | 297 | 298 |
| K | V | S | E | L | P | V | L | M | G | E | R | F | E | V | L | V | E | V | N | D | N | K | P | F | D | L | V | T | L |
| 299 | 300 | 301 | 302 | 303 | 304 | 305 | 306 | 307 | 308 | 309 | 310 | 311 | 312 | 313 | 314 | 315 | 316 | 317 | 318 | 319 | 310 | 321 | 322 | 323 | 324 | 325 | 326 | 327 | 328 |
| P | V | S | Q | M | G | M | A | I | A | P | F | D | K | P | H | P | V | M | R | I | Q | P | I | A | I | S | A | S | G |
| 329 | 330 | 331 | 332 | 333 | 334 | 335 | 336 | 337 | 338 | 339 | 340 | 341 | 342 | 343 | 344 | 345 | 346 | 347 | 348 | 349 | 350 | 351 | 352 | 353 | 354 | 355 | 356 | 357 | 358 |
| A | L | P | D | T | L | S | S | L | P | A | L | P | S | L | E | G | L | T | V | R | K | L | Q | L | S | M | D | P | M |
<tr<359 | 360 | 361 | 362 | 363 | 364 | 365 | 366 | 367 | 368 | 369 | 370 | 371 | 372 | 373 | 374 | 375 | 376 | 377 | 378 | 379 | 380 | 381 | 382 | 383 | 384 | 385 | 386 | 387 | 388 | </tr>
| L | D | M | M | G | M | Q | M | L | M | E | K | Y | G | D | Q | A | M | A | G | M | D | H | S | Q | M | M | G | H | M |
| 389 | 390 | 391 | 392 | 393 | 394 | 395 | 396 | 397 | 398 | 399 | 400 | 401 | 402 | 403 | 404 | 405 | 406 | 407 | 408 | 409 | 410 | 411 | 412 | 413 | 414 | 415 | 416 | 417 | 418 |
| G | H | G | N | M | N | H | M | N | H | G | G | K | F | D | F | H | H | A | N | K | I | N | G | Q | A | F | D | M | N |
| 419 | 420 | 421 | 422 | 423 | 424 | 425 | 426 | 427 | 428 | 429 | 430 | 431 | 432 | 433 | 434 | 445 | 436 | 437 | 438 | 439 | 440 | 441 | 442 | 443 | 444 | 445 | 446 | 447 | 448 |
| K | P | M | F | A | A | A | K | G | Q | Y | E | R | W | V | I | S | G | V | G | D | M | M | L | H | P | F | H | I | H |
| 449 | 450 | 451 | 452 | 453 | 454 | 455 | 456 | 457 | 458 | 459 | 460 | 461 | 462 | 463 | 464 | 465 | 466 | 467 | 468 | 469 | 470 | 471 | 472 | 473 | 474 | 475 | 476 | 477 | 478 |
| G | T | Q | F | R | I | L | S | E | N | G | K | P | P | A | A | H | R | A | G | W | K | D | T | V | K | V | E | G | N |
| 479 | 480 | 481 | 482 | 483 | 484 | 485 | 486 | 487 | 488 | 489 | 490 | 491 | 492 | 493 | 494 | 495 | 496 | 497 | 498 | 499 | 500 | 501 | 502 | 503 | 504 | 505 | 506 | 507 | 508 |
| V | S | E | V | L | V | K | F | N | H | D | A | P | K | E | H | A | Y | M | A | H | C | H | L | L | E | H | E | D | T |
| 509 | 510 | 511 | 512 | 513 | 514 | 515 | 516 |
| G | M | M | L | G | F | T | V |
Stabilisation of Cu1001
|
Stabilisation of Cu1002
|
Stabilisation of Cu1003
|
Stabilisation of Cu1004
|
Stabilisation of Act1005
|
[13]
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.