From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8)
Introduction
Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC 8) is an enzyme that plays a role in controlling gene expression. Specifically, it catalyzes the removal of an acetyl group off of the ε-amino-lysine sidechain of N-terminal core of Histone proteins. By removing the acetate ion, the reclaimed positive charge on the lysine sidechain is able to interact with the negative charge on the DNA. As a result, DNA will bind more tightly to the histone protein reducing transcription and expression.
Function
Histones
Acetylation
|
Homology
Classes
Sequence Alignment
Structural Highlights
Zinc Ion
Key Residues
Binding Pocket
Mechanism
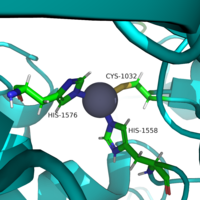 Similar to many serine and zinc proteases, HDAC8 uses a mechanism with a "catalytic triad." Instead of the Asp-His-Ser, HDAC8 uses the His to coordinate a H2O nucleophile.
Relevance
Gene Expression
Disease
HDAC Inhibitors
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
|
References

