Introduction
Histones
Histones are a family of basic, positively charged proteins that associate with DNA inside the nucleus to help condense the DNA into chromatin [1]. The nuclear DNA is wrapped around the histone in order to fit in the nucleus. Nucleosomes are chromatin beads made up of DNA wrapped around eight histone proteins, or a histone octamer [1]. Each histone octamer is made up of two copies of four different histone proteins, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 [1].
Epigenetics
Histone Deacetylase
HDAC8
Histone Deacetylase 8
Structure
General Structure Information
Inhibitor
Potassium Binding Site
Deacetylation
Zn2+ Metal Ion Mechanism
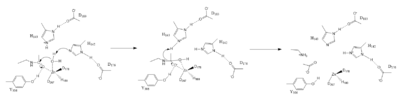
Figure 1. Mechanism of HDAC8
Active Site
Disease
HDACis

