scene=
Introduction
selectivity pore
Disease
Relevance
Calcium signaling
Structural highlights and mechanism
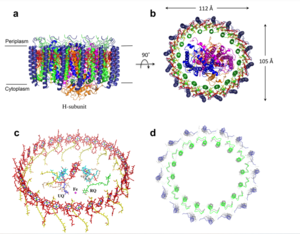
The MCU is a dimer of dimers, described as tetrameric truncated pyramid. The uniporter has only a single strong binding site located in the selectivity pore with specificity for
Calcium, near the surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Activity of the uniporter is dependent on membrane potential and calcium concentration. Calcium from the cytoplasm enters the mitochondrial innermemnrane space through the mitochondrial membrane and is passed to the mitochondrial matrix via the MCU.
Transmembrane Domain
The transmembrane domain is on the inner mitochondrial membrane open to the inner membrane space. The small pore, highly specific for calcium binding is located in the , in TM2 (transmembrane 2) while TM 1 (transmembrane 1) surrounds the pore. The transmembrane domain exhibits four fold rotational symmetry. The domain swapping of TM1 of one subunit with the TM2 of the neighboring subunits allows for a tight packing in the transmembrane connectivity. It is important that the selectivity pore is small, allowing only a dehydrated calcium molecule to interact with the 5 ampier wide glutamate ring. Approximately one helical turn below the glutamate ring of the selectivity filter, there is a tyrosine ring coming a 12 ampier wide pore allowing high conductivity. The wider opening allows calcium to rehydrate.
Coiled coil
N-terminal Domain