DNA Polymerase Theta
From Proteopedia
|
Contents |
Structural Description
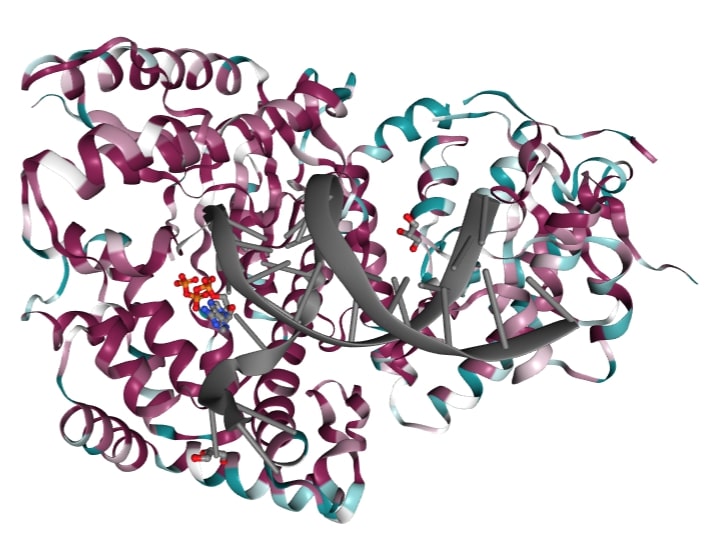
The polymerase domain of DNA polymerase theta (QM1) is a member of the A-family of polymerases which includes Pol I and T7 DNA polymerase. A-family polymerases contain . These motifs allow for identification of A-family polymerases based on their amino acid sequence. In addition to the A-family motifs, the finger-palm-thumb subdomains that are typical of many polymerases are also conserved in QM1. The finger subdomain coordinate the DNA template and the incoming nucleotide while the palm subdomain performs catalysis and the thumb subdomain contacts the double stranded DNA. Within these subdomains exist disordered structural inserts that are not present in bacterial homologs. These inserts impart unique properties to QM1; insert 1 increases processivity while inserts 2 and 3 facilitate the ability of QM1 to bypass DNA lesions that typically block synthesis by other A-family polymerases. This error prone synthesis makes QM1 more functionally similar to Y-family polymerases.
Beyond the canonical polymerase folds, QM1 also possesses a vestigial exonuclease domain that no longer performs proof-reading activities. This domain also contains structural inserts that are thought to contact the more distant helicase-like and central domains of full-length polymerase theta (see Function).
It is thought that QM1 may function as a dimer, as dimerization interfaces were identified in the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure. The presence of dimerization in solution has not yet been confirmed.
Key Interactions
Function
Full length polymerase theta consists of an N-terminal helicase-like domain that is connected to the C-terminal polymerase domain by a central linker region.
 Polymerase theta is a DNA double strand break repair protein. Double strand breaks can occur as a result of both exogenous (ionizing radiation) and endogenous (reactive oxygen species, replication fork collapse) damage. To repair breaks, polymerase theta employs theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ), which is a form of alternative end-joining (altEJ). TMEJ begins with pairing of microhomologies in 3' single stranded overhangs that have been exposed through 5' end resectioning at the site of the break. If the microhomologies are internal to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA, the resulting flaps will be removed and a deletion will be introduced. If microhomologies arise from brief templated synthesis with a more distant strand, insertions will occur. Once microhomologies are aligned, pol theta synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps on either side of the microhomologies.
Polymerase theta is a DNA double strand break repair protein. Double strand breaks can occur as a result of both exogenous (ionizing radiation) and endogenous (reactive oxygen species, replication fork collapse) damage. To repair breaks, polymerase theta employs theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ), which is a form of alternative end-joining (altEJ). TMEJ begins with pairing of microhomologies in 3' single stranded overhangs that have been exposed through 5' end resectioning at the site of the break. If the microhomologies are internal to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA, the resulting flaps will be removed and a deletion will be introduced. If microhomologies arise from brief templated synthesis with a more distant strand, insertions will occur. Once microhomologies are aligned, pol theta synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps on either side of the microhomologies.
Sequence Conservation
The sequence of QM1 is highly conserved as it belongs to a distinct family of polymerases. The majority of conserved residues reside in the interior of the channel that contacts the DNA and incoming nucleotide indicating that these regions are critical to polymerase function. Less sequence conservation is observed in the exterior alpha helices as the residues are exposed at the surface and alpha helices can tolerate more variation in amino acid composition than other secondary structural elements.
Relevance
References
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
