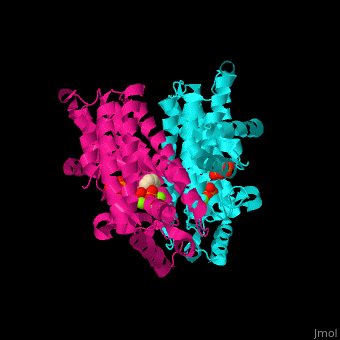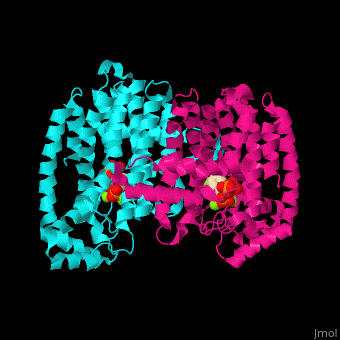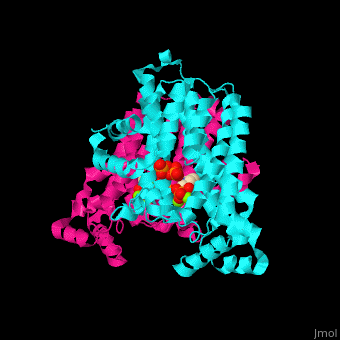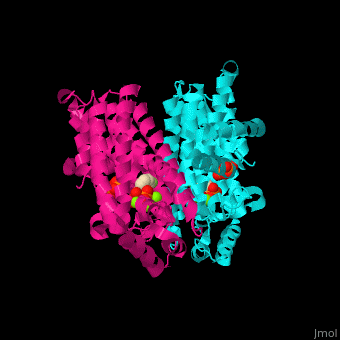Function
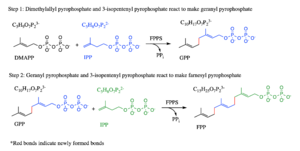
Farnesyl pyrophospate synthase (FPPS), also named Farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FPS), is a chain elongation enzyme that catalyzes carbon-carbon formation in two consecutive condensation reactions that convert one equivalent of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and two equivalents of isopentyl diphosphates (IPP) into one equivalent of Farnesyl pyrophospate. (FPP) [1] In the first step, IPP and its isomer DMAPP react to form a ten-carbon geranyl diphosphate (GPP), while in the second step, the product geranyl diphosphate from the first step and an additional IPP molecule react to make FPP (see diagram). It is an essential enzyme in the biosynthesis of mevalonate, isoprenoids, and sterols in a variety of organisms. FFPS has been studied in conjunction with different parasites. TcFPPS refers to FPPS in the Typanosoma cruzi parasite while LmFPPS refers to FPPS in the Leishmania major parasite. Bisphosphonates have been shown to inhibit FPPS and are currently being used as antiparasitic drugs as well as a treatment for various bone diseases.
Relevance
FPS bisphosphonate inhibitors (like zoledronic acid) are used as drugs for treatment of bone resorption diseases[2]. FPS inhibitor Alendronate or Fosamax is used in treatment of osteoporosis[3].
Structural insights
FPS contains and binds ; see also , (PDB code 2opm)[4], water molecules are shown as red spheres.
3D structures of farnesyl diphosphate synthase
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase 3D structures