We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
TonB
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
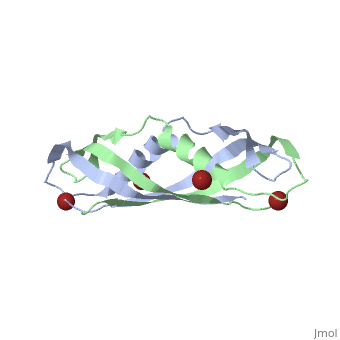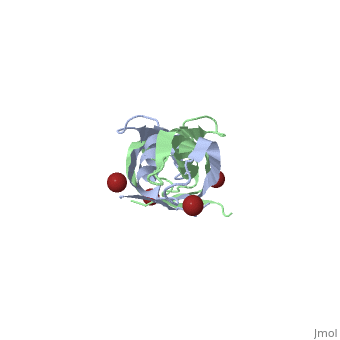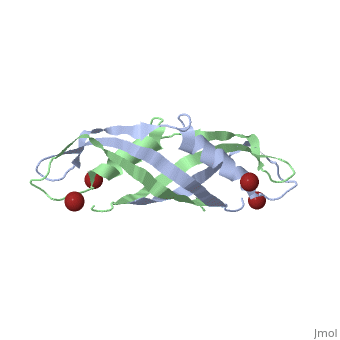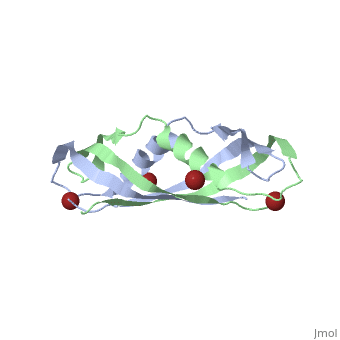
3D structures of TonB
1ihr, 1qxx, 1u07 – EcTonB C terminal – Escherichia coli
1xx3, 5lw8 - EcTonB C terminal – NMR
2grx - EcTonB + ferrichrome-iron receptor
2ivz - EcTonB + colicin-E9 peptide
2gsk - EcTonB C terminal + vitamin B12 transporter BtuB
2k9k – TonB2 C terminal – Listonella anguillarum
6fip - PaTonB C terminal – Pseudomonas aeruginosa - NMR
6i97 - PaTonB C terminal + TonB-dependent receptor
5lw8, 6sly - TonB C terminal – Helicobacter pylori - NMR
References
- ↑ Pawelek PD, Croteau N, Ng-Thow-Hing C, Khursigara CM, Moiseeva N, Allaire M, Coulton JW. Structure of TonB in complex with FhuA, E. coli outer membrane receptor. Science. 2006 Jun 2;312(5778):1399-402. PMID:16741125 doi:312/5778/1399
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Postle K, Kastead KA, Gresock MG, Ghosh J, Swayne CD. The TonB Dimeric Crystal Structures Do Not Exist In Vivo. MBio. 2010 Dec 21;1(5). pii: e00307-10. PMID:21179522 doi:10.1128/mBio.00307-10
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kampfenkel K, Braun V. Topology of the ExbB protein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6050-7. PMID:8449962
- ↑ Wiener MC. TonB-dependent outer membrane transport: going for Baroque? Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Aug;15(4):394-400. PMID:16039843 doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2005.07.001
- ↑ Held KG, Postle K. ExbB and ExbD do not function independently in TonB-dependent energy transduction. J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5170-3. PMID:12193634
- ↑ Cadieux N, Bradbeer C, Kadner RJ. Sequence changes in the ton box region of BtuB affect its transport activities and interaction with TonB protein. J Bacteriol. 2000 Nov;182(21):5954-61. PMID:11029413
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Shultis DD, Purdy MD, Banchs CN, Wiener MC. Outer membrane active transport: structure of the BtuB:TonB complex. Science. 2006 Jun 2;312(5778):1396-9. PMID:16741124 doi:312/5778/1396