Background
Ligands
Significance
Structure
Heterotrimeric G-Protein Structure
Novel Characteristics
MRGPRX2 demonstrates novel characteristics compared to other class A GPCRs. These structural motif differences contribute to a surface ligand binding rather than a ligand binding deep within the helices. To demonstrate this difference in depth binding, MRGPRX2 is compared to 5HT2AR, another class A GPCR with more conserved structural motifs.
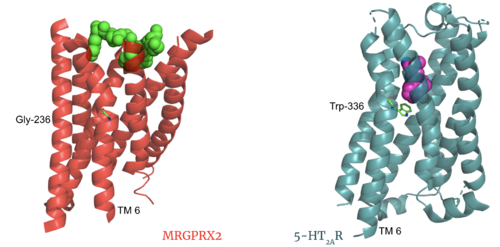
Comparison of ligand Cortistatin-14 binding in MRGPRX2 (left) and binding in 5HT2AR (right)
Toggle Switch
PIF/LLF Motif
DRY/ ERC Motif
MRGPRX2 has an rather than the typically conserved E/DRY Motif. The amino acid residue shift from TYR-174 to CYS-128 has spatial arrangement implications where the helices are more compact in MRGPRX2 without the TYR to physically push the TMP helices apart.
Sodium Site
The MRGPRX2 consists of ASP-75 and GLY-116 compared to the previously conserved residues in this binding pocket. Other class A GPCRs demonstrate a larger binding pocket with a higher negative character allowing for a suitable environment for sodium ions to bind. In MRGPRX2, this pocket lacks the same amount of with the shift to a glycine residue rather than typical negative residues. The helices for the MRGPRX2 in the binding pocket are also more collapsed making this pocket less accessible for sodium ions.
Disulfide Bonds
Further Information
NPxxY Motif
The in the NPxxY motif are pivotal for receptor activation in all Class A GPCRs. This motif is conserved in the MRGPRX2 receptor with residues VAL-231, ASP-75, ASN-275, and TYR-279.
Function
Before Activation
After Activation
Clinical Relevance
3D Structures
References


