Sandbox Reserved 1790
From Proteopedia
This page, as it appeared on March 17, 2023, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
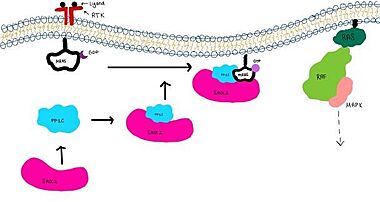
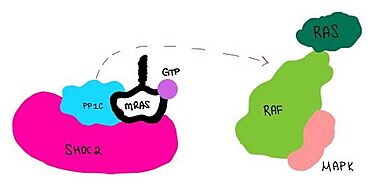
IntroductionSHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a ternary complex formed by the individual proteins: SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. Formation of this complex begins with a signal binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase receptor(RTK). This causes membrane bound MRAS to exchange GDP for GTP. From here the complex comes together and is able to dephosphorylate the RAF complex leading to further downstream signaling effects.
Overall StructureSHOC2
PP1C
MRASis a membrane bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now undergoes a conformational change of the switch I and switch II regions. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind more easily with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex.
Key Ligand InteractionsSHOC2 and PP1CPP1C binds to SHOC2 on its leucine rich region(LRR). Specifically, on two broad surfaces between LRR2 and LRR5 and between LRR7 and LRR11. Five main hydrogen bonds are made: E56-R182, E167-R203, E54-K180, R187-H178, R188-E155. The binding regions can also be shown as acidic and basic patches on and . The corresponding patches interact to form a . SHOC2 and MRASMRAS is initially bound to GDP causing it to be in its inactive state. This form cannot bind to the SHOC2-PP1C complex due to steric clashing. Once GDP is exchanged for GTP to activate the protein, conformational changed occur withing the switch I and switch II regions to allow MRAS to interact with SHOC2. These interactions include hydrogen bonds of and pi stacking. The primary hydrogen bonds are R288-Q71 and R177-E47. Pi staking occurs at R104-R83. PP1C and MRASThe interactions between PP1C and MRAS are mediated by four main hydrogen bonds: R188-D48, M190-Q35, D197-H53, Q198-K36. It is unclear whether PP1C must bind to SHOC2 before MRAS binds or if PP1C and MRAS can bind to SHOC2 at the same time. Signaling Pathway
Disease RelevanceCancerRASopathiesFuture Studies3D structures of lysophosphatidic acid receptor4z34, 4z35, 4z36 - hLPA1 + antagonist - human References
Student ContributorsMadeline Gilbert Inaya Patel Rushda Hussein | ||||||||||||