From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
H. sapiens mIgM B Cell Receptor
|
Introduction
Structure
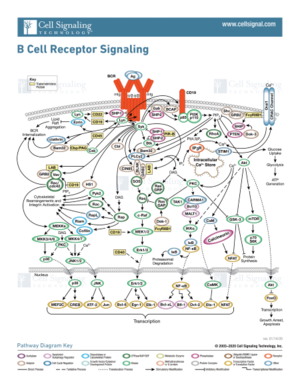 Figure 2. The Signal pathway for the response to an antigen by the B-cell receptor. Illustration reproduced courtesy of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. ( www.cellsignal.com).
Antigen Binding Site
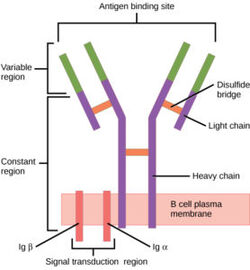 Figure 1. Overview of the human B Cell Receptor and its structural components. Used with permission under Wikimedia Commons. The binding of an antigen to the human B Cell receptor is identical to other common soluble antibodies (such as IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, or IgD). The antibody portion of the B Cell Receptor is roughly "Y" shaped and consists of two identical and two identical chains creating two similar epitope binding regions[1] (figure 1). Two antigen molecules can bind independent of one another to produce a response. Matching with standard FABs, the Ig portion has constant and variable region. The stem of the "Y" is a (Fc) composed of only heavy chain interactions[1]. The two heavy chains then branch at a flexible . These interact individually with one light chain creating two Fab fragments or branches of the "Y"[1]. Light and heavy chains are held together via weak intermolecular forces and disulfide bridges[1]. Each then terminates with two (Fv). These variable regions consist of hyper-variable loops, desired random coils of amino acids selected for specific recognition of a desired antigen [1]. Binding to an antigen is determined based on intermolecular interactions to the hyper variable loops, and selectivity is provided by unique hyper variable loop sequences. Due to the identical structure of Fab fragments, BCR will recognize antigens in the same manner as do free antibodies.
Heavy Chain Interactions (Iga and IgB)
Transmembrane Interactions
Function
Proposed Conformational Changes
Signal Pathway
|
Medical Relevancy
Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001.
Disease
B-cells and their respective receptors play an important role in the immune response. Therefore, if the receptors were to not function properly, there would be damaging consequences. Autoimmune disease is suggested to occur when somatic cells are recognized as foreign antigens and the body tries to eliminate them. Although the exact mechanism of disease has not been provided, it is thought that B-cell receptors are an essential part of these diseases due to their function and role in the immune systems. B-cell receptors are improperly recognizing somatic cells from different tissues depending on the disease and elicit the production of antibodies against them (autoantibodies). This causes destruction of these cell types. Examples of these diseases include rheumatoid arthritis where the lining of joints is targeted and degraded, multiple sclerosis which targets the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve cells, type 1 diabetes mellitus where the insulin producing cells are targeted for destruction, and systematic lupus erythematosus where multiple organ systems are targeted (skin, brain, lungs, and kidneys are common targets).
Therapeutics
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, et al. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2001.


