Function
14-3-3 proteins (PRS) are conserved regulatory proteins which bind to a multitude of signaling proteins like kinases phosphatases and transmembrane receptors. The name 14-3-3 derives from their elution pattern via chromatography.[1]
Disease
Elevated levels of PRS are found in patients with Creutzfeld-Jakob disease (CJD). PRS are associated with Parkinson Disease (PD) and with Alzheimer Disease (AD) based on their localization and their binding to PD and AD-associated proteins.
Relevance
PRS are tested as biomarkers for CJD, PD and AD.
Structural highlights
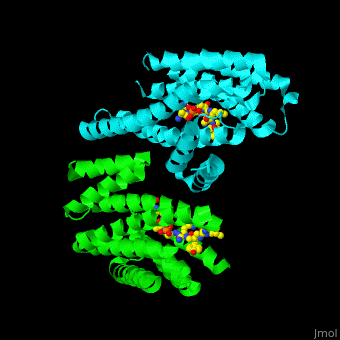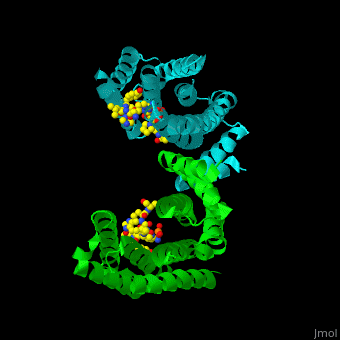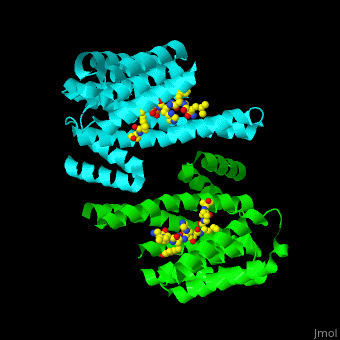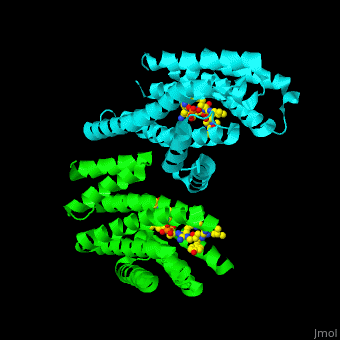
PRS are homo- and heterodimers containing . Three of the helices form the (3 helices of chain A are in red and 3 helices of chain B are in magenta). .
3D structures of 14-3-3 protein
14-3-3 protein 3D structures