From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link Protein 4DIU: Structure, Function, and Significance in Biological Systems
The protein 4DIU has been identified and characterized as a potential esterase enzyme based on in-depth analyses including bioinformatics, molecular docking studies, and laboratory experiments. Online tools such as BLAST, Dali, and InterPro often matched 4DIU with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. This suggests that its function involves hydrolysis of esters. In part to data from Swiss Dock, 4DIU is predicted to have binding sites with an affinity to substrates such as acetate, butyrate, phosphate, proline, decanoate, and dodecanoate. The protein 4DIU was grown, harvested, and isolated in a laboratory. SDS-PAGE analysis was used to confirm the identity of the protein via molecular weight. Once identified the enzyme's activity on the substrate p-nitrophenyl acetate was measured. This substrate was chosen because many hydrolases have an affinity for it and can hydrolyze the substrate.
| [1] [2]
Overview of Esterase
The role in the body this would play based on results. Any potential implications of the enzyme if disrupted based on findings and related enzymes.
Proposed Function
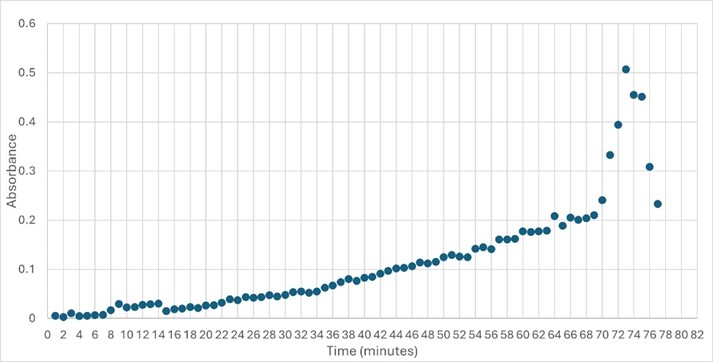
This protein has alpha/beta-hydrolase activity and is of the esterase family. The SPRITE, BLAST, InterPro, and Dali Search along with other bioinformatics analyses consistently matched with carboxylesterases and other esterase-like proteins. SPRITE provided proteins that had similar residues in the active site of the enzyme. Multiple of the matching proteins were esterases and had an RMSD value of <0.5. The RMSD value gives insight into how similar the overlapping sections for the unknown and known proteins are. A value of less than 2 is desired when choosing proteins for reference as a value closer to zero means less deviation between sites. SwissDock and Chimera allowed for protein-ligand docking studies. Many of the highlighted interactions were ester-containing ligands and others were susceptible to hydrolysis. The isolated protein was introduced to 10 mM p-nitrophenyl acetate in a buffer with a pH of 6. Enzyme activity was measured, and the data was consistent with other hydrolases.
Structural highlights
Highlight the data that helped you come to your conclusion here including any relevant figures. Make sure to include potential substrates and binding sites.
|
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
[1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.

