User:Michael Skovbo Windahl/sandbox
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||
| 3e2t, resolution 1.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , , , | ||||||||
| Activity: | Tryptophan 5-monooxygenase, with EC number 1.14.16.4 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
This is a sandbox
Tryptophan hydroxylase is an iron and tetrahydrobiopterin dependent monooxygenase which belongs to the enzyme family of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases.
Contents |
Tryptophan binding
is bound in the active site. It is bound by polar contacts in the amino acid end and by hydrophobic interactons in the side chain end.
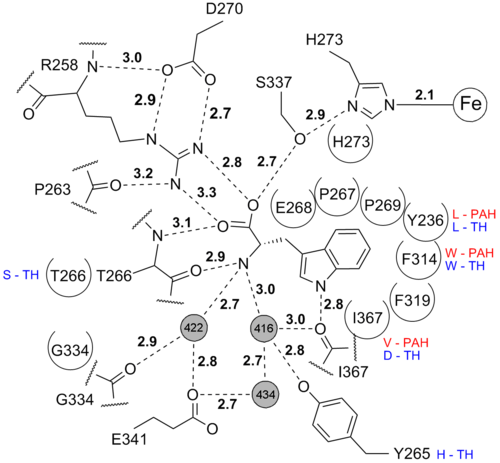
Iron coordination
|
The by 2 histidines, one glutamate and one imidazole from the solvent. This coordination is called the 2-histidine-1-glutamate facial triad iron coordination and is seen in many mononuclear non-heme iron(II)enzymes[1]. In this structure Glu317 coordinates the iron in a partial bidentate manner. The more common (the resting state) for the 2-His-1-Glu iron coordination is seen in the structure of human TPH1 1mlw.
Imidazole binding
The is bound to the iron and to the protein chain through two brigding water molecules. The first water molecule makes hydrogen bonds to Gly235 and to Leu237 while the other water molecule makes hydrogen bonds to His252 and Glu274. This binding is similar to the binding in structure of the catalytic domain of human TPH1 pdb code 1mlw. See the dihydrobiopterin binding
References
- ↑ Koehntop KD, Emerson JP, Que L Jr. The 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad: a versatile platform for dioxygen activation by mononuclear non-heme iron(II) enzymes. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2005 Mar;10(2):87-93. Epub 2005 Mar 1. PMID:15739104 doi:10.1007/s00775-005-0624-x

