User:Tilman Schirmer/Sandbox 211
From Proteopedia
PleD
Overview
|
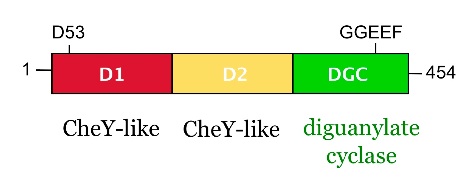
from Caulobacter crescentus is a response regulator with an unorthodox catalytic, diguanylate cyclase, output domain. It is composed of a canonical CheY-like response regulator receiver () domain,
a Rec-like () adaptor domain,
and a C-terminal domain that confers the catalytic acitvity.
The GGDEF domain is named after the highly conserved (in PleD it is GGEEF) that locates to a β-hairpin.
Substrate binding
|
The motif is part of the as identified in the structure of PleD in complex with . The GGDEF domain binds only one GTP substrate molecule. For the reaction to proceed, two GTP loaded GGDEF domains have to align antiparallely.
Complete active site
| Theoretical Model: The protein structure described on this page was determined theoretically, and hence should be interpreted with caution. |
After binding of the , it is believed that two GGDEF domains associate antiparallely to form a catalytically competent dimer (, ). Then, by inter-molecular nucleophilic in-line attack of the O3' atom onto the α-phosphorous of the other GTP substrate molecule, two phosphodiester bonds are formed under release of two pyrophosphate molecules.