From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link p53R2
|
|
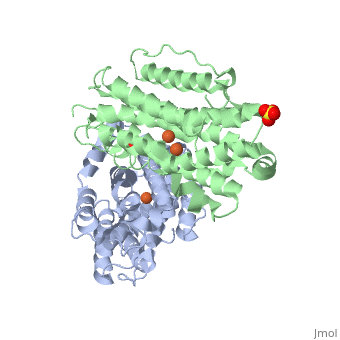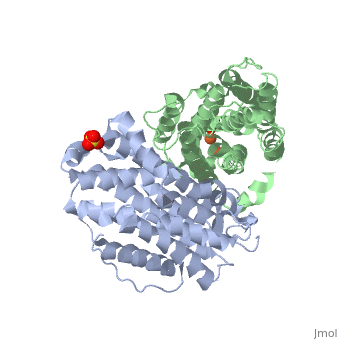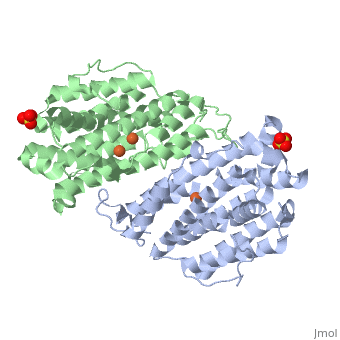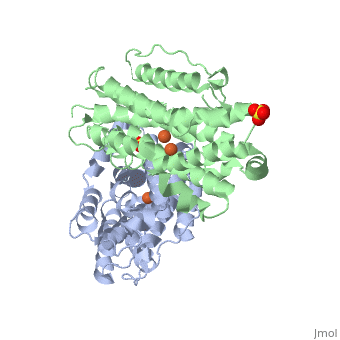
| 3hf1, resolution 2.60Å ()
|
| Ligands:
| ,
|
| Gene:
| RRM2B, P53R2 (Homo sapiens)
|
| Activity:
| Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase, with EC number 1.17.4.1
|
| Related:
| 1xsm, 2uw2, 1w69, 1w68
|
|
|
|
|
| Resources:
| FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum
|
| Coordinates:
| save as pdb, mmCIF, xml
|
P53R2 is an oxydoreductase composed of 351 residues. It is a small subunit of the ribonucleotide reductase (RNR).
RNR catalyses the reduction of the four nucleotides to desoxyribonucleotides. It exists three classes of RNR. Class I RNR is a tetramer composed of the two types of subunits with stoichiometry α2β2 and three subunits have been identified in mammals :
- Large (α) subunit M1 that contains the enzyme active site
- Small (β) subunit M2 that contains a dinuclear iron site, it’s the regulatory subunit
- P53R2, the last identified (in 2000), which is transactivated by p53 in response to DNA damage in cells during the G0-G1 cell cycle phase
M2 and p53R2 interact with M1 through the C-terminal binding domain. These two subunits share more than 80% sequence identity. But the few differences between the two are not unimportant, as it’s explained below.
The first X-ray crystal structure of p53R2 has a resolution of 2,6 Å and permits to describe its structure and also to show the structural differences with the M2 subunit.
Structure and function