We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Birrer Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to their corresponding aldehydes and ketones through a mechanism that involves the removal of hydrogen. In the oxidation mechanism, ADH is momentarily associated with nicontinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which functions as a cosubstrate. The mechanism of the reaction is below: CH3CH2OH + NAD+ Image:Arrow.jpg CH3COH (acetaldehyde) + NADH + H+
Replace the PDB id (use lowercase!) after the STRUCTURE_ and after PDB= to load
and display another structure.
| |||||||||
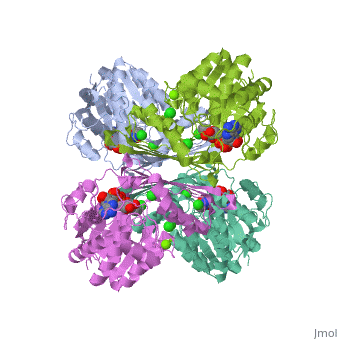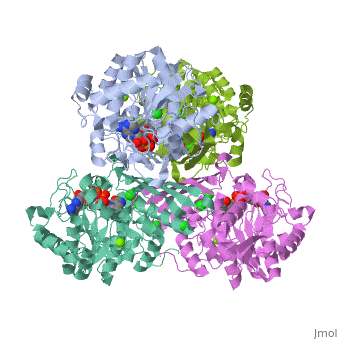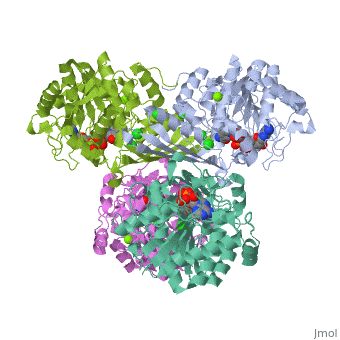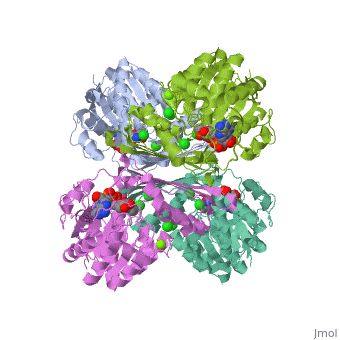
| 3cin, resolution 1.70Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | , , | ||||||||
| Gene: | TM1419, TM_1419 (Thermotoga maritima MSB8) | ||||||||
| Activity: | Inositol-3-phosphate synthase, with EC number 5.5.1.4 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum, TOPSAN | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||