Interleukin-10
From Proteopedia
Contents |
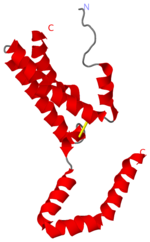
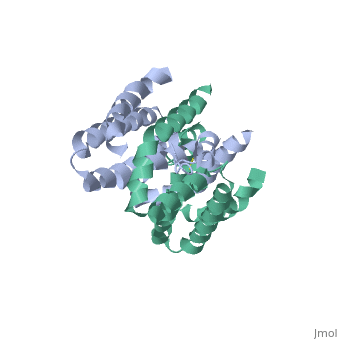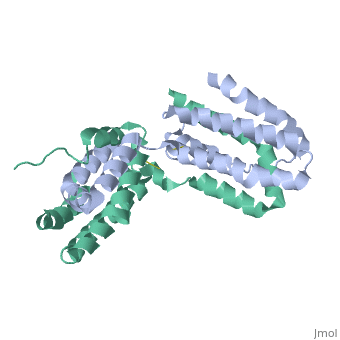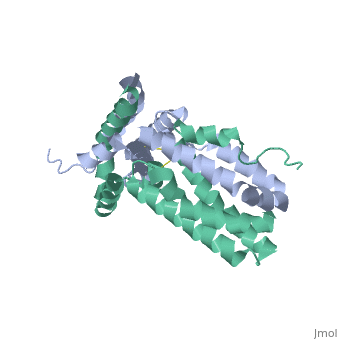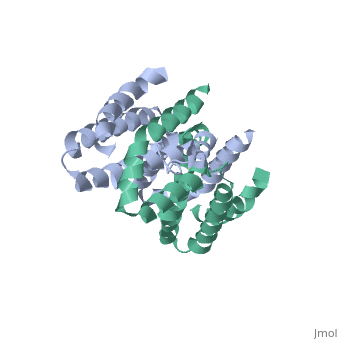
Interlukin-10 2H24
Crystal structure of human IL-10
Interleukin-10 is in the class cytokine.[1] Cytokines have many funtions such as from antiinflammatory cytokines,cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor and proinflammitory cytokines[2]. Interleukin-10 is a very powerful anti-inflammatory cytokine. It is also a cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor. These are the reasons that IL-10 is investigated for its role in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) as well as those with osteoarthritis (OA)[3]. RA is an autoimmune disorder that affects the synovial tissues via chronic synovitis. Chronic synovitis often results in joint destruction due to re-absorption of bone and the distruction of cartilage[4] [5]. IL-10 is found to spontaneously be produce in synovial tissue of patients with RA and OA but not in normal synovial tissue. The variation in secretion of IL-10 is thought to be at about 75% under the control of the genetics of the individual[6]. When IL-10 is blocked there is a increase in the proinflammatory cytokines, namely TFN-α and Il-1β Make a link to the wiki website that talks about cytokines. Make a link to RA
|
| Please do NOT make changes to this Sandbox until after April 23, 2010. Sandboxes 151-200 are reserved until then for use by the Chemistry 307 class at UNBC taught by Prof. Andrea Gorrell. |
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Shelly Huebert, Andrea Gorrell, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky, Michal Harel