6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS)
From Proteopedia
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst and on display at the Molecular Playground.
Polyketides are a large and structurally diverse class of natural products produced by bacteria, fungi, and plants. They exhibit a wide variety of biological activities including antibiotic, antitumor, anticancer, among others.
In Nature, polyketides are synthesized by large multifunctional proteins called polyketide synthases (PKSs).. Among several characterized PKSs, the biosynthesis of the polyketide Core of erythromycin A, 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-dEB), has provided the paradigm for understanding the structure and function of the PKSs that are responsible for assembling complex polyketides .
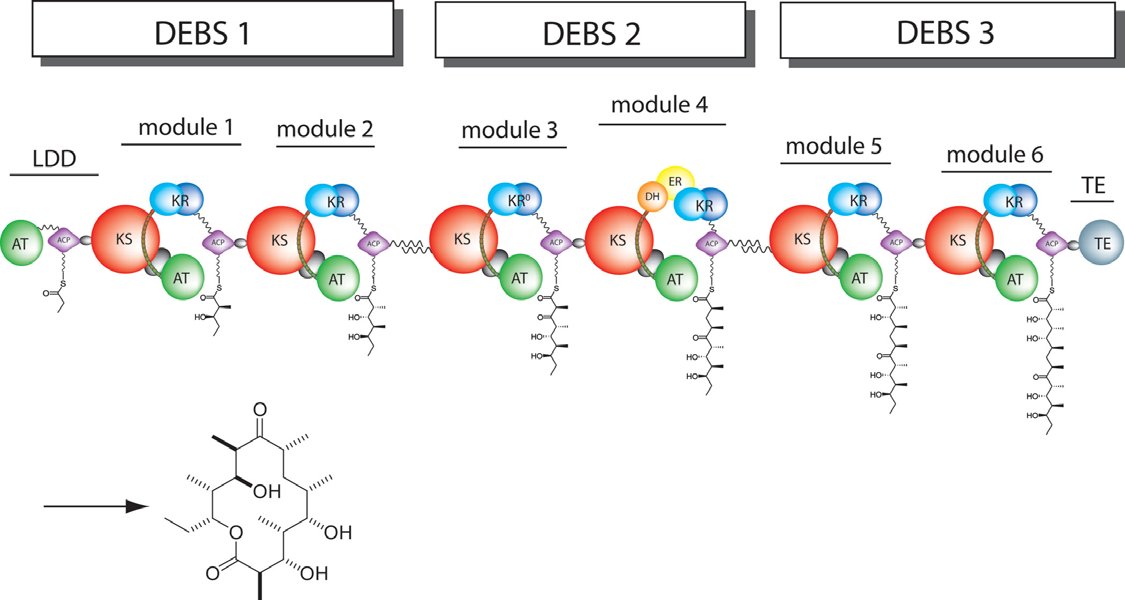
The 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase (DEBS), which catalyzes the formation of 6-dEB, consists of three large subunits, DEBS1, DEBS2 and DEBS3, each containing two modules and above 300 kD in size. There are 2 domains in the N-terminal loading module, responsible for priming the synthase with a proprionate starter unit, and 26 domains in the six extender modules, Each extender module contains at least three essential domains: a ketosynthase (KS), an acyl transferase (AT) and an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In detail, the AT domain selects the appropriate carbon extender unit and transfers the units from acyl-CoA onto the phosphopantetheine arm of ACP. The KSdomain accepts the polyketide chain from the previous module and catalyzes chain elongation reaction by adding an ACP-bound extender unit through decarboxylative condensation.
After the extender unit is added, it can be further processed by optional tailoring domains, including ketoreductases (KRs), dehydratases (DHs), and enoyl reductases (ERs), to yield a hydroxyl, enoyl, or methylene group at the -position. Finally, the thioesterase (TE) domain that located at the C-terminus of DEBS module 6 promotes the macrocyclization event which releases the final product, 6-dEB. .
Contents |
KS-AT
Molecular Playground banner: KS-AT is responsible for one round of chain extension, "the carbon adding worker".
|
ACP
Molecular Playground banner: carrying the carbon extender unit, "the communicator".
|
DH
Molecular Playground banner: make modification on beta-keto-acyl-ACP, "the decorator".
|
TE
Molecular Playground banner: cyclize the molecule, "the closer".
|
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Tsung-Yi Lin, Alexander Berchansky, Lawrence Sheringham Borketey, Joel L. Sussman, Jon Amoroso, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky