From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link=[Image:Opening 1igt.png|450px|left|thumb| Intact Immunoglobulin, 1igt]]
|
|
| Structura IGG B12 uman: o monstra pentru un potential vaccin HIV, 1hzh
|
| Ligands:
| , , , ,
|
| Structural annotation:
|
| Resources:
| CATH : 1Hzhh04, 1Hzhh03, 1Hzhh02, 1Hzhh01, 1Hzhk04, 1Hzhk03, 1Hzhk01, 1Hzhk02, 1Hzhl02, 1Hzhl01, 1Hzhm02, 1Hzhm01
SCOP : d1hzhh4, d1hzhh2, d1hzhh1, d1hzhh3, d1hzhk3, d1hzhk1, d1hzhk4, d1hzhk2, d1hzhl2, d1hzhl1, d1hzhm2, d1hzhm1
|
|
|
|
| Resources:
| FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum
|
| Coordinates:
| save as pdb, mmCIF, xml
|
Antibodies, also known as Immunoglobulins (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These glycoproteins serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other antigens. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody and . It is this specificity that has made a critical component in laboratory and medical research.
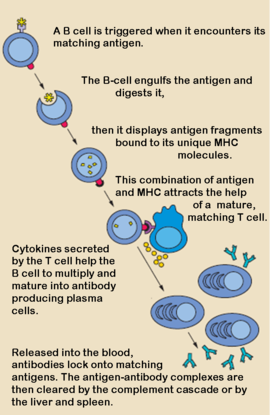
Production of Antibodies by Plasma Cells
Template:STRUCTURE 1igt


