Sandbox Mati
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Coagulation Factor XIa
Introduction
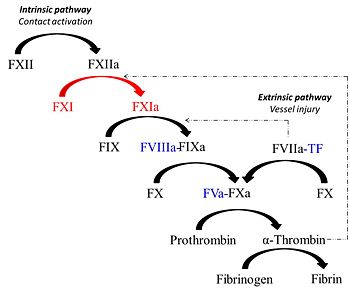
Factor XIa is unique protease derived from the activation of the coagulation zymogen, factor XI. Factor XIa partcipates in the procoagulant response via contact activation pathway. Synthesized by the liver similar to most vitamin K-dependent coagulation proteins, the zymogen, factor XI circulates in plasma as a 160 kDa disulfide-linked homodimer in complex with high molecular weight kininogen (HK)(REF). Studies show that factor XI is a substrate for various plasma proteins such as factor XIIa, thrombin, meizothrombin and factor XIa (via autoactivation). Proteolysis of the Arg369-Ile370 bond generates the active enzyme factor XIa which in turn cleaves its substrate factor factor IX to produce the serine protease factor IXa. Template:STRUCTURE 3bg8
Protein Structure
Each dimeric subunit of factor XIa exhibit similar amino acid composition of about 607 residues constituting five main domains. The N-terminus of each subunit contains 4 apple domains (A1, A2, A3 and A4) which are characterized by approximately 90 or 91 amino acid motifs. The C-terminus contain the trypsin-like catalytic domain. Together with Prekallikrein (PK) a monomeric homolog of factor XIa, they belong to the PAN (plasminogen, apple, nematode) module family which all have a conserved N-terminal apple domain.