Translocation domain
From Proteopedia
The Colicin translocation domain is found at the T terminus of the colicin protein. This structure is involved in the recruitment of a group of proteins, either from the Tol system or the Ton system, after the receptor binding domain of the colicin has bound to an outer membrane receptor of the target cell, such as BtuB. The proteins recruited by the T domain are then responsible in some way for the translocation of the colicin into the cytoplasm of the target cell, through a mechanism as yet unidentified, although a few hypotheses about how this occurs do exist.
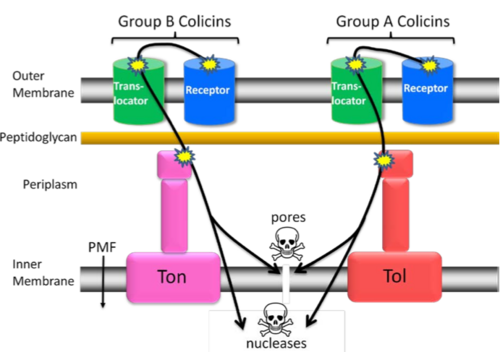
A diagram showing a generalised translocation path of the colicins from group A and group B into the cytoplasm, not showing all types of cytotoxic activity[1]
References
- ↑ Kleanthous C. Swimming against the tide: progress and challenges in our understanding of colicin translocation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Dec;8(12):843-8. Epub 2010 Nov 9. PMID:21060316 doi:10.1038/nrmicro2454
