From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link Introduction
|
|
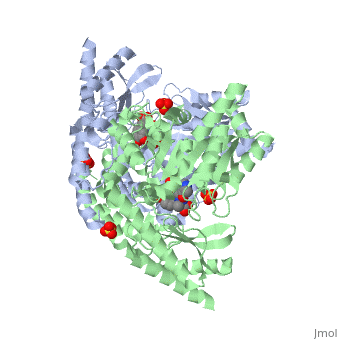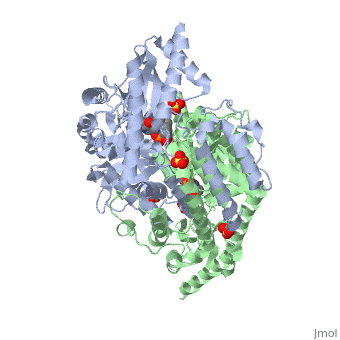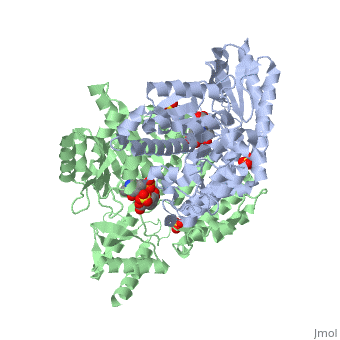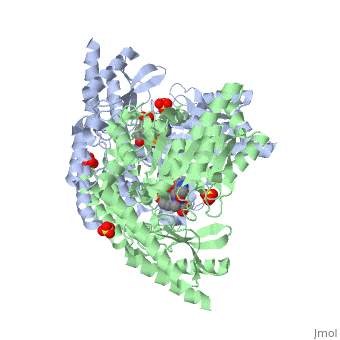
| 1js3, resolution 2.25Å ()
|
| Ligands:
| , ,
|
| Activity:
| Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase, with EC number 4.1.1.28
|
| Related:
| 1js6
|
| Structural annotation:
|
| Resources:
| CATH : 1Js3A01, 1Js3A03, 1Js3A02, 1Js3B03, 1Js3B02, 1Js3B01
InterPro : Ipr010977, Ipr002129, Ipr015421, Ipr015424, Ipr015422
Pfam : PF00282
SCOP : d1js3a_, d1js3b_
UniProt : P80041
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Resources:
| FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum
|
| Coordinates:
| save as pdb, mmCIF, xml
|
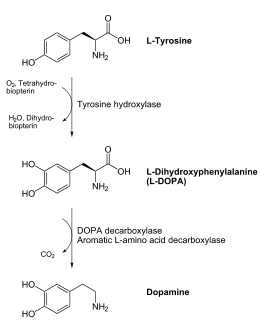
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, tryptophan decarboxylase, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, AAAD) is an approximately 52 kDa protein that belongs to the aspartate aminotransferase family (fold type 1) of PLP-dependent enzymes. The catalytically active form of the enzyme exists as a homodimer, typical of this class of enzymes. It is responsible for the synthesis of dopamine and serotonin from L-DOPA and L-5- hydroxytryptophan, respectively. Due to its role in neurotransmitter synthesis, DOPA decarboxylase has been implicated in Parkinson's Disease, a disease thought to be the result of the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. Currently, treatment for the disease is aimed at DOPA decarboxylase inhibition, which would allow greater amounts of exogenously administered L-DOPA to reach the brain.
Structure