Aldolase
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||
| 4ald, resolution 2.80Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligands: | |||||||||
| Activity: | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, with EC number 4.1.2.13 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase
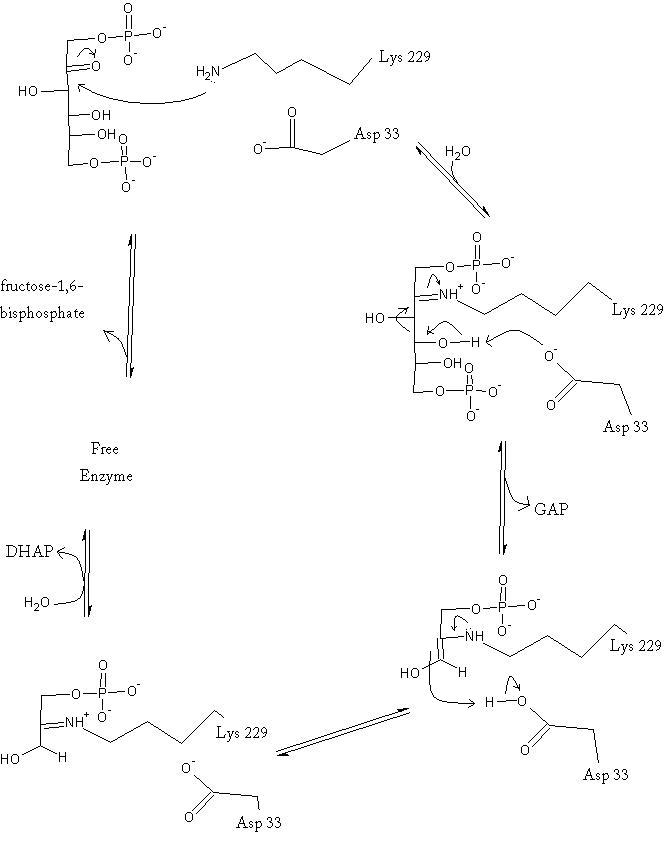
Introduction and Structure
| |||||||||||
Kinetics
Isotopic labelling has revealed the rate-determining step for the reaction. Either the carbon-carbon bond cleavage or the release of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate comprise the slow step of the catalysis reaction; however, studies do indicate that the GAP release is likely the slowest step.[3]
It has been shown that aldolase is inhibited allosterically by oxidized glutathione, which is an oxidizing species biologically present. The glutathione oxidizes a thiol 25 angstroms from the catalytic site, which subsequently causes a drop in catalytic activity. In addition, the enzyme shows no positive cooperativity, despite being an oligomer. In fact, kinetics data actually show that the enzyme exhibits negative cooperativity. Thus the catalysis is highly compartmentalized within each subunit and binding causes little distal change of the enzymes structure.[5]
Regulation
The regulation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is not well understood, but the understanding is every-increasing. As it is currently observed, aldolase C appears to be regulated mainly by the gene expression--the concentration of mRNA in the cytoplasm.[6] It is also known that adenosine 3',5'-cyclicmonophosphate (cAMP) affects the expression of the gene. cAMP concentration has been positively correlated with aldolase C expression. It is believed that cAMP acts upon a section of the promotor region, distal element D, causing the transcriptional promoter, NGFI-B, to bind. Once bound, the promoter activates the transcription of the gene coding for fructose bisphosphate aldolase.[7] Given the inhibitory effects of an oxidant in the presence of aldolase, it is possible that this could be a mechanism of regulation of the enzyme. The deactivation that accompanies the oxidation of the surface thiol of Cys72 could be used intracellularly to slow the catalysis of the enzyme and regulate glycolysis.[5]
3D structures of Aldolase
Fructose–1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
1ojx, 1ok6 – TptFBPA – Thermoproteus tenax
3qrh – EncFBPA – Encephalitozoon cuniculi
3qm3 - FBPA – Campylobacter jejuni
3q94 – FBPA – Bacullus anthracis
3c4u– HpFBPA – Helicobacter pylori
1zah, 1fdj, 1ewd, 1ewe, 1ex5, 1ado - rFBPA – rabbit
3dfn, 3dfp, 3dfq, 3dft, 2bv4, 3b8d – rFBPA (mutant)
3kx6 – FBPA – Babesia bovis
3gak – GiFBPA – Giardia intestinalis
3ekl, 3ekz – MtFBPA – Mycobacterium tuberculosis
2qap, 1epx – LmFBPA – Leishmania mexicana
1a5c – PfFBPA – Plasmodium falciparum
2iqt – FBPA – Porphyromonas gingivalis
2fjk – FBPA – Thermus caldophilus
1xfb, 1qo5, 2ald, 1ald – hFBPA – human
1gyn, 1l6w, 1dos, 1zen – EcFBPA - Escherichia coli
1f2j – FBPA – Trypanosoma brucei
1fba – FBPA – Drosophila melanogaster
FBPA binary complex
2yce, 1ok4 – TptFBPA + reaction intermediate
1w8s – TptFBPA + FBP
3mbd – EncFBPA + phosphate
3mbf - EncFBPA + FBP
3n9r, 3n9s, 3c52, 3c56 - HpFBPA + inhibitor
3mmt – FBPA + FBP – Bartonella henselae
1zai - rFBPA + FBP
6ald - rFBPA (mutant) + FBP
2quv - rFBPA + phosphate
2qut - rFBPA + reaction intermediate
3dfo, 3dfs, 2quu - rFBPA (mutant) + reaction intermediate
1j4e - rFBPA (mutant) + substrate
2ot0 – rFBPA + Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein C-terminal
2ot1, 1zaj, 1zal – rFBPA + inhibitor
3lge – rFBPA + Sorting Nexin-9
3gay – GiFBPA + inhibitor
3gb6 – GiFBPA + FBP
3elf – MtFBPA + FBP
2qdg - LmFBPA + FBP
2qdh – LmFBPA + inhibitor
2eph, 2pc4 – PfFBPA + BPTRAP C-terminal
4ald – hFBPA + FBP
1rv8, 1rvg – FBPA + metal – Thermus aquaticus
1b57 – EcFBPA + oxamate
Tagatose–1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
3myo, 3myp, 3mhf– SpTBPA – Streptococcus pyogenes
3mhg - SpTBPA + reaction intermediate
3kao – SaTBPA – Staphylococcus aureus
1gvf - EcTBPA
Fuculose–1-phosphate aldolase
2opi – FPA – Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron
2flf, 2fk5 – TtFPA - Thermus thermophilus
1e46, 1e47, 1e48, 1e49, 1e4a, 1e4b, 1e4c, 1dzu, 1dzw, 1dzx, 1dzy, 1dzz – EcFPA (mutant)
4fua – EcFPA + oxamate
Deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase
3r12, 3r13, 1pvt, 1o0y – TmDERA – Thermotoga maritime
3ndo – MsDERA – Mycobacterium smegmatis
3ng3 – MsDERA + aldehyde
2a4a – DERA – Plasmodium yoelii
1vcv – DERA – Pyrobaculum aerophilum
1p1x – EcDERA
1jcj, 1jcl – EcDERA (mutant) + reaction intermediate
1n7k – DERA – Aeropyrum pernix
1mzh – AaDERA - Aquifex aeolicus
Dehydroneopterin aldolase
3r2e – DHNPA – Yersinia pestis
2o90 – EcDHNPA + neopterin
2nm2, 2nm3, 1u68, 2dhn - SaDHNPA + neopterin
1rri, 1rrw, 1rry, 1rs2, 1rs4, 1rsd, 1rsi, 1dhn - SaDHNPA + inhibitor
1z9w – MtDHNPA
1sql – DHNPA + guanine – Arabidopsis thaliana
HPCH/HPAI aldolase
3qz6 – HPA – Desulfitobacterium hafniense
2v5j – EcHPA
2v5k – EcHPA + oxamate
Sialic acid aldolase
3lbm – EcSAA
3lcf, 3lcg, 3lch, 3lci, 3lcl, 2wnq, 2wo5 - EcSAA (mutant)
3lbc – EcSAA + L-arabinose
2wnn – EcSAA + pyruvate
2wnz, 2wkj - EcSAA (mutant) + pyruvate
2wpb - EcSAA (mutant) + pyruvate + inhibitor
3lcx - EcSAA L-KDO (mutant)
3lcw - EcSAA L-KDO (mutant) + hydroxypyruvate
Oxoadipate aldolase
3noj – PpCHA-ALD – Pseudomonas putida
Oxovalerate aldolase
1nvm – OVA + acetaldehyde dehydrogenase - Pseudomonas
Deoxydephosphogluconate aldolase
3nzr – DDPGA – Vibrio fischeri
2nuw, 2nux – SaDDPGA – Sulfolobus acidocaldarius
1vlw – TmDDPGA
1w37 - SsDDPGA – Sulfolobus solfataricus
1fwr - EcDDPGA (mutant)
DDPGA complex
1nuy – SaDDPGA + pyruvate
1wa3 - TmDDPGA + pyruvate
1w3i - SsDDPGA + pyruvate
1w3n - SsDDPGA + gluconate
1w3t - SsDDPGA + gluconate + pyruvate
1eua - EcDDPGA + pyruvate
Deoxydephosphooctonate aldolase
2ef9, 2nws, 2nx1, 2nx3, 2nxg, 2nxh, 1t99 – AaDDPOA (mutant)
1x8f – EcDDPOA
3fs2 – DDPOA – Bruciella melitensis
3e9a – DDPOA – Vibrio cholerae
2qkf – DDPOA – Neisseria meningitides
DDPOA binary complex
1fxp – AaDDPOA + Cd
1pck, 1fwn, 1fws - AaDDPOA + PEP
1pcw, 1pe1, 1jcx - AaDDPOA + inhibitor
1lrn - AaDDPOA (mutant) + Cd
2nwr, 1t96, 1lro - AaDDPOA (mutant) + PEP
3e12 – AaDDPOA + KDO8P
1x6u - EcDDPOA + KDO8P
1q3n - EcDDPOA + PEP
1phq, 1phw, 1pl9 - EcDDPOA + substrate analog
DDPOA tertiary complex
1fy6 - AaDDPOA + arabinose + Cd
1jcy, 1fwt, 1fww, 1fxq - AaDDPOA + PEP + sugar
2a2i, 1zha, 1zji, 1t8x, 1lrq - AaDDPOA (mutant) + PEP + arabinose
2a21 - AaDDPOA + PEP + phosphate
Deoxydephosphogalactonate aldolase
2v81 – EcKDPGAL
2c0a – EcKDPGAL (mutant)
2v82 – EcKDPGAL + 2-keto-deoxy-galactose
Deoxydephosphoheptonate aldolase
1vr6 – TmKDPHAL
Deoxygalactarate aldolase
1dxe – EcDGA
1dxf – EcDGA + pyruvate
Aldolase class II
3ocr – ALDII – Pseudomonas syringae
2vws – EcALDII
2vwt – EcALDII + pyruvate
Sphingosin-1-phosphate aldolase
3mc6 – SCDPL1 (mutant) – yeast
Rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase
1gt7 – EcRPA
2v9g, 2v9o, 2uyu, 2uyv, 2v9e, 2v9f, 2v9i, 2v9l, 2v9m, 2v9n, 2v29, 2v2a, 2v2b, 1ojr – EcRPA (mutant)
Oxoglutarate aldolase
3m6y – OGA – Bacillus cereus
LsrF aldolase
3gkf – EcLsrFA
3glc, 3gnd – EcLsrFA + ribose derivative
Threonine aldolase
1lw4, 1lw5 – TmThrA + amino acid
1svv – ThrA – Leishmania major
Phenylserine aldolase
1v72 – PpFSA
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Voet, D, Voet, J, & Pratt, C. (2008). Fundamentals of biochemistry, third edition. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- ↑ Protein: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from human (homo sapiens), muscle isozyme. (2009). Retrieved from http://scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Gefflaut, T., B. Casimir, J. Perie, and M. Willson. "Class I Aldolases: Substrate Specificity, Mechanism, Inhibitors and Structural Aspects." Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol.. 63. (1995): 301-340.
- ↑ Dalby A, Dauter Z, Littlechild JA. Crystal structure of human muscle aldolase complexed with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate: mechanistic implications. Protein Sci. 1999 Feb;8(2):291-7. PMID:10048322
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sygusch, J., and Beaudry, D. "Allosteric communication in mammalian muscle aldolase." Biochem. J.. 327. (1997): 717-720.
- ↑ Paolella, G, Buono, P, Mancini, F P, Izzo, P, and Salvatore, F. "Structure and expression of mouse aldolase genes." Eur. J. Biochem.. 156. (1986): 229-235.
- ↑ Buono, P, Cassano, S, Alfieri, A, Mancini, A, and Salvatore, F. "Human aldolase C gene expression is regulated by adenosine 30,50-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in PC12 cells." Gene. 291. (2002): 115-121.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Sophie Mullinix, Jaime Prilusky, Austin Drake, David Canner