This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Tom Sandbox
From Proteopedia
| |||||||
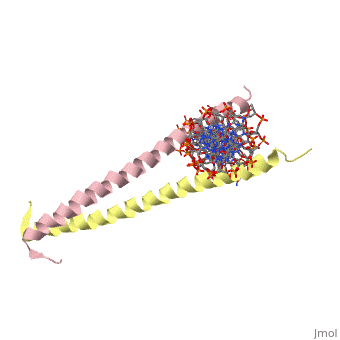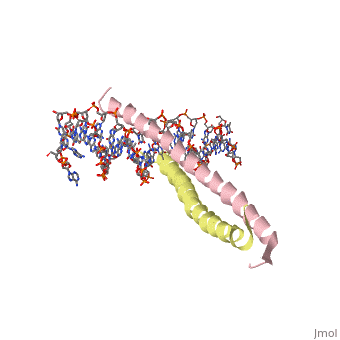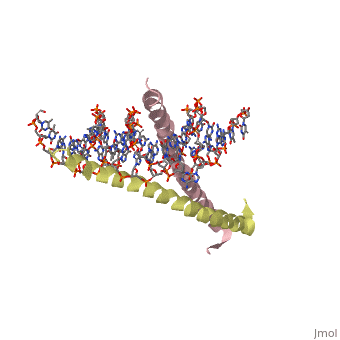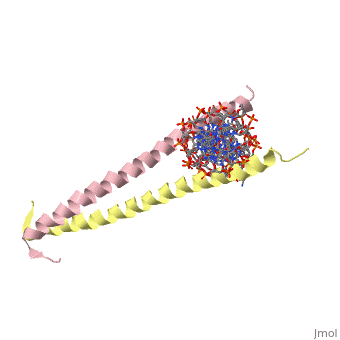
| 2zta, resolution 1.80Å () | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Standard Residues: | |||||||
| |||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||
Contents |
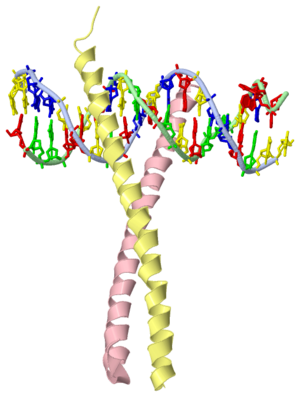
GCN4 - The Leucine Zipper
Blah blah information about leucine zipper GCN4.
| |||||||||
| 1ysa, resolution 2.90Å () | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum | ||||||||
| Coordinates: | save as pdb, mmCIF, xml | ||||||||
Structure
GCN4 (PDB 2zta by itself, 1ysa bound to DNA) is a eukaryotic transcription factor first isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also known as Baker's Yeast. CITE CITE CITE It is composed of two identical 52 residue alpha helix chains that grouped together to form a dimer. The dimer binds through interlocking leucine amino acids in the C terminal ends, while pinching in on the major groove of DNA in the N terminal end. The X-ray structure of the 33-residue polypeptide corresponding to the leucine zipper of GCN4 was determined by Peter Kim and Thomas Alber[1].
Binding
The Leucine Zipper
Binding with DNA
Function
See Also
Reference
- ↑ Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith G.; Pratt, Charlotte W. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd Ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2008.