Group:MUZIC:Zyxin
From Proteopedia

|
Contents |
ZYXIN
Zyxin, meaning a joining [1], is a LIM domain protein of the zyxin/ajuba family, encode by the gene ZYX [1], that codes for a protein of 84 kDa [1]. Zyxin, is an important scaffolding protein and component of the actin linking functional module. Zyxin has a proline-rich amino-terminus and a carboxy-terminus containing three LIM domains which are recognized historically as zinc-binding motifs (see figure at right) [2]. The LIM domains of zyxin have been shown to bind to factors that control gene transcription [3] and they function as regulatory domains for controlling protein-protein interactions with components involved in cell-cell junction assembly [4,5]. Zyxin is also thought to be autoregulated by an intramolecular interaction between the LIM domains and the VASP binding site [5].
Function and structure
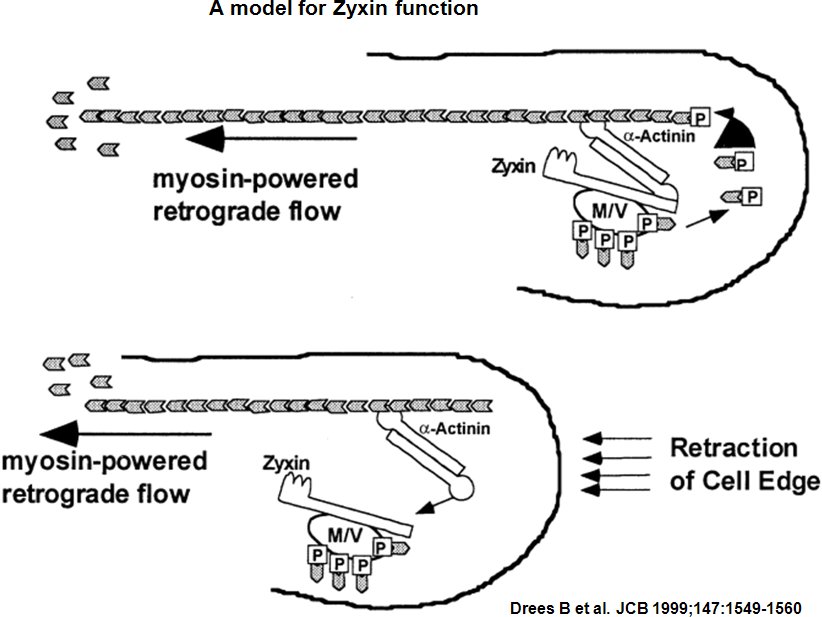
Zyxin is a zinc-binding phosphoprotein that concentrates at cell-cell or cell-matrix adhesion sites, stress fiber bundles and along the actin cytoskeleton [2] [3]. Zyxin is specifically found in more mature adhesion sites (e.g. focal adhesions) [4], which are actin-rich structures that enable cells to adhere to the extracellular matrix [5] and its absence in early adhesions (e.g. focal complexes) is commonly used to distinguish the 'age' of an adhesion [6]. It is postulate, that Zyxin may be a component of a signal transduction pathway that mediates adhesion-stimulated changes in gene expression by similarity [7]. Zyxin has an N-terminal proline-rich domain and three LIM domains in its C-terminal half. The proline-rich domain may interact with SH3 domains of proteins involved in signal transduction pathways while the LIM domains are likely involved in protein-protein binding. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same isoform [8]. The main function of zyxin is to form a bridge between the adhesion components at the cell membrane and the internal cytoskeleton [9]. Zyxin is vital for coordinating matrix-dependent cues with actin dynamics; for example, within stress fibers and focal adhesions (FAs), zyxin acts as a mechanosensor that binds to areas where forces are applied [10] [11] [12]. Not only is zyxin binding proportional to the mechanical force (e.g. decreased traction reduces zyxin-binding) but zyxin recruitment and stability at adhesion sites is tension-dependent [13] [14]. Cellular adaptation to mechanical stress also involves redistribution of zyxin from FAs to stress fibers, which causes stress fiber thickening [15]. Mislocalization of zyxin leads to defects in cell migration and spreading [16] [17] and its absence leads to increased cellular motility [18] preseumably through reduced adhesive strength [19]. Zyxin influences actin organization and assembly around FAs by recruiting Ena/VASP [20] [21] [22]. The initiation factor-independent mechanism, by which Ena/VASP may subsequently generate new actin filaments is still unknown [23].
Interactions
Performing yeast two-hybrid analysis system, Yu and Luo found that myopodin interacts with zyxin both in vitro and in vivo and that this interaction leads to slower migration of prostate cancer cells and reduced invasiveness (Yu YP, Luo JH, 2006). Zyxin interacts with the E6 Protein from Human Papillomavirus Type 6 and this interaction results in its nuclear translocation [24]. Zyxin has been shown also to interact with ENAH [25], [26], LASP1 [27], LATS1 [28], Actinin, alpha 1 [29], [30] and Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein [31].
References
- ↑ Sadler I, Crawford AW, Michelsen JW, Beckerle MC. Zyxin and cCRP: two interactive LIM domain proteins associated with the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1573-87. PMID:1469049
- ↑ Crawford AW, Beckerle MC. Purification and characterization of zyxin, an 82,000-dalton component of adherens junctions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5847-53. PMID:2005121
- ↑ Sadler I, Crawford AW, Michelsen JW, Beckerle MC. Zyxin and cCRP: two interactive LIM domain proteins associated with the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1573-87. PMID:1469049
- ↑ Beningo KA, Dembo M, Kaverina I, Small JV, Wang YL. Nascent focal adhesions are responsible for the generation of strong propulsive forces in migrating fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 2001 May 14;153(4):881-8. PMID:11352946
- ↑ Macalma T, Otte J, Hensler ME, Bockholt SM, Louis HA, Kalff-Suske M, Grzeschik KH, von der Ahe D, Beckerle MC. Molecular characterization of human zyxin. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 6;271(49):31470-8. PMID:8940160
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Ballestrem C, Kam Z, Geiger B. Early molecular events in the assembly of matrix adhesions at the leading edge of migrating cells. J Cell Sci. 2003 Nov 15;116(Pt 22):4605-13. PMID:14576354 doi:10.1242/jcs.00792
- ↑ Macalma T, Otte J, Hensler ME, Bockholt SM, Louis HA, Kalff-Suske M, Grzeschik KH, von der Ahe D, Beckerle MC. Molecular characterization of human zyxin. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 6;271(49):31470-8. PMID:8940160
- ↑ Gene ID: 7791
- ↑ Beckerle MC. Zyxin: zinc fingers at sites of cell adhesion. Bioessays. 1997 Nov;19(11):949-57. PMID:9394617 doi:10.1002/bies.950191104
- ↑ Lele TP, Pendse J, Kumar S, Salanga M, Karavitis J, Ingber DE. Mechanical forces alter zyxin unbinding kinetics within focal adhesions of living cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006 Apr;207(1):187-94. PMID:16288479 doi:10.1002/jcp.20550
- ↑ Colombelli J, Besser A, Kress H, Reynaud EG, Girard P, Caussinus E, Haselmann U, Small JV, Schwarz US, Stelzer EH. Mechanosensing in actin stress fibers revealed by a close correlation between force and protein localization. J Cell Sci. 2009 May 15;122(Pt 10):1665-79. Epub 2009 Apr 28. PMID:19401336 doi:10.1242/jcs.042986
- ↑ Yoshigi M, Hoffman LM, Jensen CC, Yost HJ, Beckerle MC. Mechanical force mobilizes zyxin from focal adhesions to actin filaments and regulates cytoskeletal reinforcement. J Cell Biol. 2005 Oct 24;171(2):209-15. PMID:16247023 doi:10.1083/jcb.200505018
- ↑ Lele TP, Pendse J, Kumar S, Salanga M, Karavitis J, Ingber DE. Mechanical forces alter zyxin unbinding kinetics within focal adhesions of living cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006 Apr;207(1):187-94. PMID:16288479 doi:10.1002/jcp.20550
- ↑ Colombelli J, Besser A, Kress H, Reynaud EG, Girard P, Caussinus E, Haselmann U, Small JV, Schwarz US, Stelzer EH. Mechanosensing in actin stress fibers revealed by a close correlation between force and protein localization. J Cell Sci. 2009 May 15;122(Pt 10):1665-79. Epub 2009 Apr 28. PMID:19401336 doi:10.1242/jcs.042986
- ↑ Yoshigi M, Hoffman LM, Jensen CC, Yost HJ, Beckerle MC. Mechanical force mobilizes zyxin from focal adhesions to actin filaments and regulates cytoskeletal reinforcement. J Cell Biol. 2005 Oct 24;171(2):209-15. PMID:16247023 doi:10.1083/jcb.200505018
- ↑ Drees BE, Andrews KM, Beckerle MC. Molecular dissection of zyxin function reveals its involvement in cell motility. J Cell Biol. 1999 Dec 27;147(7):1549-60. PMID:10613911
- ↑ Drees B, Friederich E, Fradelizi J, Louvard D, Beckerle MC, Golsteyn RM. Characterization of the interaction between zyxin and members of the Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein family of proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22503-11. PMID:10801818 doi:10.1074/jbc.M001698200
- ↑ Hoffman LM, Jensen CC, Kloeker S, Wang CL, Yoshigi M, Beckerle MC. Genetic ablation of zyxin causes Mena/VASP mislocalization, increased motility, and deficits in actin remodeling. J Cell Biol. 2006 Feb 27;172(5):771-82. PMID:16505170 doi:10.1083/jcb.200512115
- ↑ Ngu H, Feng Y, Lu L, Oswald SJ, Longmore GD, Yin FC. Effect of focal adhesion proteins on endothelial cell adhesion, motility and orientation response to cyclic strain. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010 Jan;38(1):208-22. Epub 2009 Oct 27. PMID:19856213 doi:10.1007/s10439-009-9826-7
- ↑ Drees B, Friederich E, Fradelizi J, Louvard D, Beckerle MC, Golsteyn RM. Characterization of the interaction between zyxin and members of the Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein family of proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22503-11. PMID:10801818 doi:10.1074/jbc.M001698200
- ↑ Hoffman LM, Jensen CC, Kloeker S, Wang CL, Yoshigi M, Beckerle MC. Genetic ablation of zyxin causes Mena/VASP mislocalization, increased motility, and deficits in actin remodeling. J Cell Biol. 2006 Feb 27;172(5):771-82. PMID:16505170 doi:10.1083/jcb.200512115
- ↑ Nix DA, Fradelizi J, Bockholt S, Menichi B, Louvard D, Friederich E, Beckerle MC. Targeting of zyxin to sites of actin membrane interaction and to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 14;276(37):34759-67. Epub 2001 Jun 6. PMID:11395501 doi:10.1074/jbc.M102820200
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Ballestrem C, Kam Z, Geiger B. Early molecular events in the assembly of matrix adhesions at the leading edge of migrating cells. J Cell Sci. 2003 Nov 15;116(Pt 22):4605-13. PMID:14576354 doi:10.1242/jcs.00792
- ↑ Degenhardt YY, Silverstein S. Interaction of zyxin, a focal adhesion protein, with the e6 protein from human papillomavirus type 6 results in its nuclear translocation. J Virol. 2001 Dec;75(23):11791-802. PMID:11689660 doi:10.1128/JVI.75.23.11791-11802.2001
- ↑ Tani K, Sato S, Sukezane T, Kojima H, Hirose H, Hanafusa H, Shishido T. Abl interactor 1 promotes tyrosine 296 phosphorylation of mammalian enabled (Mena) by c-Abl kinase. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21685-92. Epub 2003 Apr 2. PMID:12672821 doi:10.1074/jbc.M301447200
- ↑ Drees B, Friederich E, Fradelizi J, Louvard D, Beckerle MC, Golsteyn RM. Characterization of the interaction between zyxin and members of the Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein family of proteins. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22503-11. PMID:10801818 doi:10.1074/jbc.M001698200
- ↑ Li B, Zhuang L, Trueb B. Zyxin interacts with the SH3 domains of the cytoskeletal proteins LIM-nebulette and Lasp-1. J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):20401-10. Epub 2004 Mar 5. PMID:15004028 doi:10.1074/jbc.M310304200
- ↑ Hirota T, Morisaki T, Nishiyama Y, Marumoto T, Tada K, Hara T, Masuko N, Inagaki M, Hatakeyama K, Saya H. Zyxin, a regulator of actin filament assembly, targets the mitotic apparatus by interacting with h-warts/LATS1 tumor suppressor. J Cell Biol. 2000 May 29;149(5):1073-86. PMID:10831611
- ↑ Reinhard M, Zumbrunn J, Jaquemar D, Kuhn M, Walter U, Trueb B. An alpha-actinin binding site of zyxin is essential for subcellular zyxin localization and alpha-actinin recruitment. J Biol Chem. 1999 May 7;274(19):13410-8. PMID:10224105
- ↑ Li B, Trueb B. Analysis of the alpha-actinin/zyxin interaction. J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 7;276(36):33328-35. Epub 2001 Jun 22. PMID:11423549 doi:10.1074/jbc.M100789200
- ↑ Harbeck B, Huttelmaier S, Schluter K, Jockusch BM, Illenberger S. Phosphorylation of the vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein regulates its interaction with actin. J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):30817-25. PMID:10882740 doi:10.1074/jbc.M005066200