Papain
From Proteopedia
| |||||||||||
Contents |
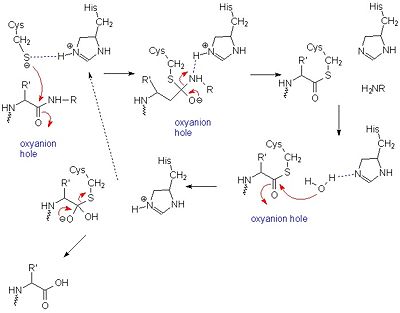
Structure
| |||||||||||
Inhibitors
| |||||||||||
Common Uses
Medicinal

Papain has been used for a plethora of medicinal purposes including treating inflammation, shingles, diarrhea, psoriasis, parasites, and many others.[22] One major use is the treatment of cutaneous ulcers including diabetic ulcers and pressure ulcers.[23] Pressures ulcers plague many bed bound individuals and are a major source of pain and discomfort. Two papain based topical drugs are Accuzyme and Panafil, which can be used to treat wounds like cutaneous ulcers.[24]
A recent New York Times article featured papain and other digestive enzymes.[25] With the number of individuals suffering from irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal issues, many people are turning toward natural digestive aid supplements like papain. The author even talks about the use of papain along with a pineapple enzyme, bromelain, in cosmetic facial masks. Dr. Adam R. Kolker (a plastic surgeon) is quoted in the article saying that "For skin that is sensitive, enzymes are wonderful." He bases these claims off the idea that proteases like papain help to break peptide bonds holding dead skin cells to the live skin cells.[26]
Commercial and Biomedical
Papain digests most proteins, often more extensively than pancreatic proteases. It has a very broad specificity and is known to cleave peptide bonds of basic amino acids and leucine and glycine residues, but prefers amino acids with large hydrophobic side chains. This non-specific nature of papain's hydrolase activity has led to its use in many and varied commercial products. It is often used as a meat tenderizer because it can hydrolyze the peptide bonds of collagen, elastin, and actomyosin. It is also used in contact lens solution to remove protein deposits on the lenses and marketed as a digestive supplement. [27] Finally, papain has several common uses in general biomedical research, including a gentle cell isolation agent, production of glycopeptides from purified proteoglycans, and solubilization of integral membrane proteins. It is also notable for its ability to specifically cleave IgG and IgM antibodies above and below the disulfide bonds that join the heavy chains and that is found between the light chain and heavy chain. This generates two monovalent Fab segments, that each have a single antibody binding sites, and an intact Fc fragment.[11]
Reference
- Kamphuis IG, Kalk KH, Swarte MB, Drenth J. Structure of papain refined at 1.65 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):233-56. PMID:6502713
Papain
3LFY, 1KHP, 1KHQ, 1CVZ, 1BQI, 1BP4, 1PPN, 1PPP, 1PIP, 1POP, 1PE6, 9PAP, 1PPD, 1PAD, 2PAD, 4PAD, 5PAD, 6PAD- Carica papaya
2CIO - Trypanosoma brucei
3E1Z - Trypanosoma cruzi
3IMA - Colocasia esculenta
1STF - Homo sapiens
Page seeded by OCA on Tue Feb 17 04:20:31 2009
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kirsten Eldredge, Jacinth Koh, Sara Kongkatong, Kyle Burch, Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Elizabeth Miller, Samuel Bray, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky