e='true' align='right' caption='RSCB-Protein Data Bank: Crystal Structure of Human Neuron Specific Enolase at 1.8 angstrom' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />
Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE) is one of the five isozymes (isoenzyme) of the
glycolysis enzyme
enolase. An enolase falls under the category of
lyase, which is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation, often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure.
[1] It is also known as a metalloenzyme, which means it contains a metal ion bound to the protein with one labile coordination site.
[2] Enolase is present in all tissues and organisms capable of glycolysis or fermentation. It is the ninth and penultimate step of glycolysis, converting 2-phosphoglycerate (2-PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
[1]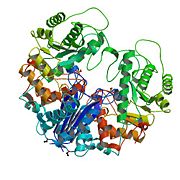
Biological Assembly Image for 1PDY Lobster Enolase
[3] Enolase has three subunits (α, β, and γ) and all of these subunits are usually found in vertebrates. Enolase α is ubiquitous, found in all cells, enolase β is muscle-specific, and the γ isozyme is found only in neurons.[4] The subunits can combine in pairs (αα, αβ, αγ, ββ, and γγ) and form the five different isozymes of enolase. It is more common to find the homodimers (αα, ββ, and γγ) in adult human cells. The αα is called enolase 1, the ββ enolase 3, and the γγ enolase 2. Each homodimer still holds their original function: Enolase 1 is non-neuronal enolase (NNE), which is found in a variety of tissues, including liver, brain, kidney, spleen, adipose, enolase 3 is muscle specific enolase (MSE), and enolase 2 neuron-specific enolase (NSE). [1]
NSE (also called Gamma-Enolase) is the most abundant form of the glycolytic enolase found in adult neurons and is thought to serve as a growth factor in neurons. NSE is useful in studying neuronal differentiation and is, therefore, a valuable tool for visualizing the entire neuron and endocrine systems. [5] NSE is mainly found in mammals, and it functions as a Phosphopyruvate dehydratase. It is specifically a hydro-lyase, which cleave carbon-oxygen bonds. In humans, NSE is encoded by the ENO2 gene.[6] The systematic name of this enzyme class is 2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase (phosphoenolpyruvate-forming). Other names in common use include nervous-system specific enolase, phosphoenolpyruvate hydrates, 2-phosphoglycerate dehydrates, 2-phosphoglyceric dehydrates, gamma-enolase, and 2-phospho-D-glycerate hydro-lyase.[7]
Structure
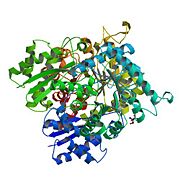
Biological Assembly Image for 1TE6 Enolase 2
[8] Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps
Mechanism
Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps
Medicine
Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps Let's see how the text wraps
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enolase
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metalloenzyme#Metalloenzymes
- ↑ X-RAY STRUCTURE AND CATALYTIC MECHANISM OF LOBSTER ENOLASE: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1PDY
- ↑ Stopped-flow studies of the reaction of d-tartronate semialdehyde-2-phosphate with human neuronal enolase and yeast enolase 1: http://www.sciencedirect.com.prox.lib.ncsu.edu/science/article/pii/S0014579310000657
- ↑ Neuron Specific Enolase: http://www.scrippslabs.com/cancer-markers-neuron-specific-enolase-nse/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enolase_2
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphopyruvate_hydratase
- ↑ Crystal Structure of Human Neuron Specific Enolase at 1.8 angstrom: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1te6


