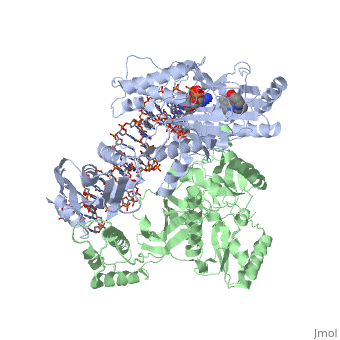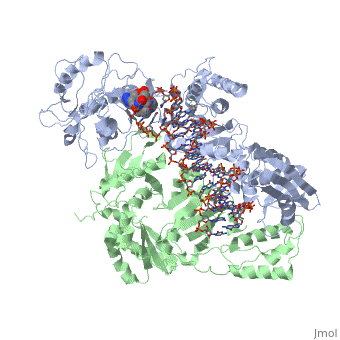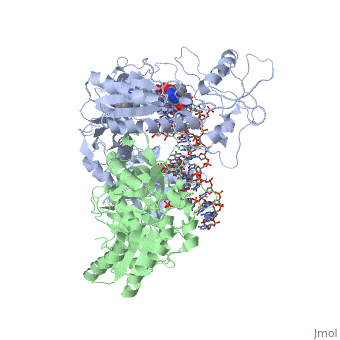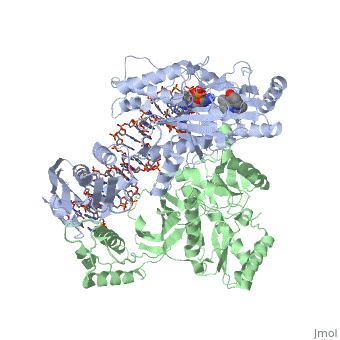
Structure of RT domains
RT is an asymmetric heterodimer composed of a 560 amino acid 66kDa subunit (p66) and a 440 amino acid 51kDa subunit (p51). The p66 and p55 domains are derived from cleavage of the same polyprotein precursor. The p51 is made from the C-terminal cleavage of the p66 subunit by HIV-1 protease. As a result, they share a common amino terminus, but the p51 subunit does not have an RNase H domain.
The p66 subunit (color) contains two enzymatically active domains, polymerase (color)and RNase H (color). This polymerase is responsible for catalyzing the polymerization of DNA using either RNA or DNA as the template. The endonucleolytic ribonuclease H (RNase H) specifically degrades the RNA strand of RNA:DNA duplexes that are produced during retrotranscription. The polymerase domain can be divided into several subdomains: the fingers (residues 1-85 and 118-155), palm (residues 86-117 and 156-236), thumb (237-318) and connecting (319-426). The RNase H domain consists of the C-terminal residues 427-560.
The p51 subunit (color) contains the same four subdomains as the polymerase domain in p66, but in different positions. The p51 subunit is therefore non-enzymatic, and instead stabilizes the proper folding of the catalytic p66 subunit. Instead of adopting an "open" catalytically-active conformation that can accommodate a nucleic acid template strand like p66, the p51 subunit is in a "closed" conformation and plays a largely structural role.[1]
NNRTIs: Anti-retroviral Drugs
RT is a prime target for anti-HIV drugs because of its essential role in the viral life cycle. A wide variety of drugs have been developed to target this enzyme in order to decrease the infectivity of HIV and slow the progression of this chronic disease. Of all anti-retroviral drugs approved by the FDA to treat individuals infected with HIV, more than half target the viral polymerase of RT.[2] One class of drugs, called non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), contain compounds that bind noncompetitively to a hydrophobic pocket near the polymerase active site. NNRTIs are a group of small hydrophobic compounds with diverse structures that inhibit HIV-1 but not HIV-2 RT.[3] Binding of these compounds inhibit the chemical step of polymerization of nucleic acid by distorting the protein.
The NNRTI Binding Pocket
Although nonnucleoside RT inhibitors are structurally diverse compounds, they all bind RT in the same location - the NNRTI hydrophobic binding pocket. The pocket is located in the palm domain of the p66 subunit between the β6-β10-β9 and β12-β13-β14 sheets approximately 10 angstroms from the three catalytic asp residues in the RT DNA polymerase domain.[4] The NNRTI BP is mostly hydrophobic in nature with considerable aromatic residues (Y181, Y188, F227, W229, and Y232), but also contains several hydrophilic residues (K101, K103, S105, D192, and E224 of the p66 subunit and E138 of the β7-β8 loop of the p51 subunit). NNRTIs most likely access the binding pocket at the p66/p51 heterodimer interface surrounded by residues L100, K101, K103, V179, and Y181 of the p66 subunit and E138 of the p51 subunit.[5] Actually, in the absence of ligand, the side chains of Y181 and Y188 point into the core, so the binding pocket doesn't exist in the free enzyme. The binding of NNRTI to HIV RT causes these side chains to shift away and make room for the ligand to enter the binding pocket.[6]
Nevirapine is a first generation NNRTI, which binds RT in a butterfly-like conformation. Several factors stabilize its interaction with RT's hydrophobic pocket, and the conformational changes it causes in RT essentially inhibits DNA synthesis. Unfortunately, single amino acid mutations in the binding pocket can significantly decrease the antiviral potency of this drug. This is true of the first generation NNRTIs, but new second generation NNRTIs are more effective against a range of drug resistant strains.