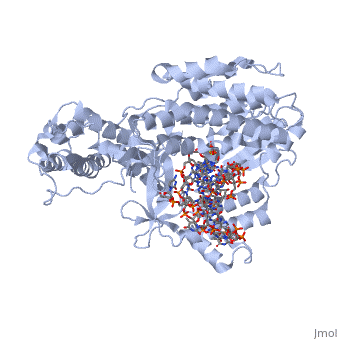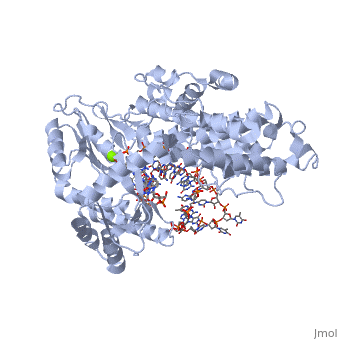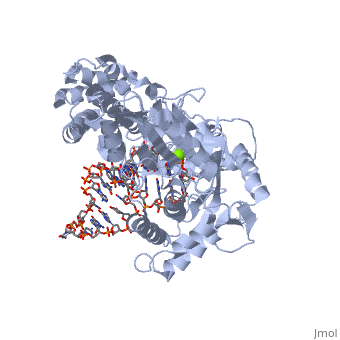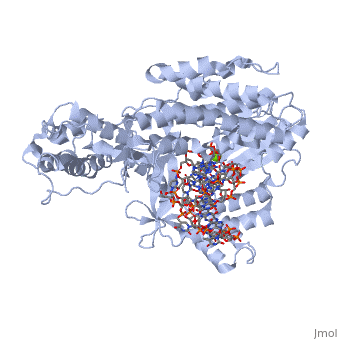
Structural Overview
TERT is a specialized reverse transcriptase belonging to the same protein family as DNA Polymerase and as such it shares the same structural motifs with a slightly different arrangement. On the whole polymerases are composed of structurally conserved motifs: the "fingers" "thumb" and "palm". TERT polymerase is similar in structure to retroviral reverse transcriptases such as HIV Reverse transcriptase. However, unlike other transcriptases TERT exists as a stable RNA-Protein complex, with an RNA molecule acting as the template molecule for dNTP addition. It is this RNA primer which allows for the high fidelity and high processivity of TERT Polymerase.
The binding site of this protein consists of a highly positively charged pocket that is configured in such a way that the DNA is inserted with its 3' end at the active site for dNTP addition. The structure shown here is a TERT complex with a DNA-RNA hairpin loop hybrid. The hybrid in the crystal structure shown here was developed in such a way that it binds similarly to the enzyme's RNA template strand, since the exact telomeric repeat sequence is not known for T. Castaneum
Major Domains
The four major domains of TERT Polymerase are as follows
Thumb
The thumb domain of the enzyme is implicated in DNA binding and processivity. The thumb domain, with the active residues Lys416 and Asn423, forms hydrogen bonds with the phosphates in the DNA backbone and keeps the base pairs oriented towards the inside of the binding pocket. A portion of the thumb domain, residues Cys390 and Gly391 are also responsible for guiding the DNA substrate into the binding pocket through bulky interactions and electron repulsion. The thumb domain runs almost completely parallel to the curvature of the DNA substrate.
Palm
The palm domain contains the active site of the enzyme. Residing in this active site are (Asp 251, 343, and 344) which form a complex with the nearby Mg2+ ion and the DNA and incoming dNTPs.
The palm domain also contains the the section of the TERT Polymerase molecule where the incoming dNTPs reside before addition to the lengthening 3' end of the DNA strand.
Finger
The finger domain in other polymerases, undergoes significant structural changes in order to bring the nucleotides present in the nucleotide binding pocket close enough to bind to the expanding DNA strand. However in polymerase the fingers seem to take a rigid closed ring conformation. This conformation seems to suggest that TERT Polymerase has a pre-formed active site, very similar in homology to that of Hepatitis C viral RNA polymerase.
This could, however, be a case where the protein was crystallized in the closed conformation. If this is the case, then it becomes clear that for the enzyme to be transitioned into the open conformation, a large amount of energy would be required. This energy could be supplied by certain accessory proteins similar to those found in conjunction with DNA Polymerases.
TRBD
The TERT RNA Binding Domain is the portion of the protein that contains the stable, complexed RNA template strand. It is here that the DNA-RNA hairpin loop in the structure binds.