Hepatocyte growth factor receptor
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor
| |||||||||||
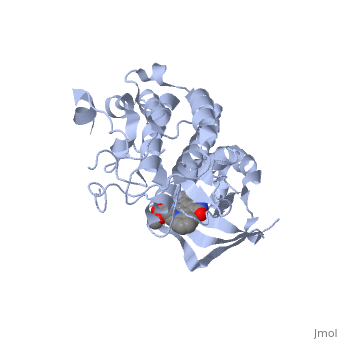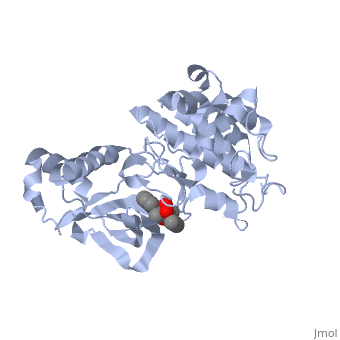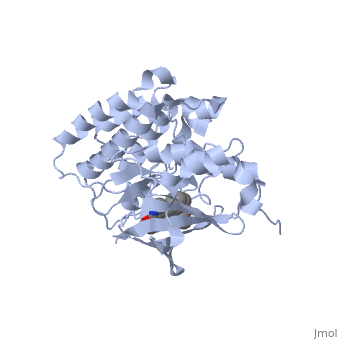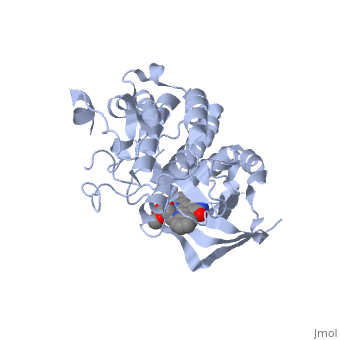
Mutated Receptor in Complex with K-252a
|
Mutation
This particular structure of the hepatocyte growth factor tyrosine kinase domain is one harboring a human cancer mutation. The two are replaced by a phenylalanine and aspartate, respectively. This mutation normally causes the receptor to be consitutively active, and is found in metastatic HNSC carcinoma. Although there is no longer phosphorylation at these sites, it is believed that the aspartate negative charge resembles the negative phosphate that would normally cause activation, and therefore keeps the protein in its active form. [10] There is a third mutation at Tyr-1194 which is substituted for a phenylalanine. This is shown to point in a the pocket formed by Lys-1198 and Leu-1195 from αE. [11] This structure is conserved in the wild
K-252a
is a staurosporine analog. Staurosporine is an inhibitor of many Ser/Thr Kinases, and has been shown to also inhibit c-Met activation by inhibiting its autophosphorylation. The structures of K-252a and staurosporine are very similar, with the main difference being that K-252a has a furanose instead of a pyranose Moiety. The binding of K-252a causes the c-Met to adopt an inhibitory conformation of the A-loop, specifically with residues . This segment blocks the place where the substrate tyrosine side chain would bind, if the protien were in an active conformation. the K-252a itself binds in the adenosine pocket, therefore inhibiting the binding of ATP. The binding of K-252a is very favorable (enthalpy change of -17.9 kcal/mol). this is probably due to polar interactions as well as a change in conformation upon binding. [12]
K-252a binds in the adensine pocket. It has four hydrogen bonds to the enzyme, with of these mimicking hydrogen bonds of an adenine base. There is a hydrogen bond between the lactam nitrogen and the carbonyl oxygen of Pro-1158, and another between the lactam carbonyl oxygen and the hydrogen of the amide of Met-1160. There are two more hydrogen bonds between the 3' hydroxyl and carbonyl oxygen and the of the A loop. [13]
There are also many hydrophobic interactions between the interface of the enzyme and K-252a. The residues involved in this are Ile-1084, Gly-1085, Phe-1089, Val-1092, Ala-1108, Lys-1110, and Leu-1140 (); Leu-1157, Pro-1158, Tyr-1159, and Met-1160 (); and Met-1211, Ala-1226, Asp-1228, Met-1229, and Tyr-1230 (). [14]
Met-1229, Met-1211 and Met-1160 all make up the for the indolocarbazole plane as they are all within van der waals distance of it. [15]
In this conformation, the peptide chain blocks the area where peptide binding would occur. Residues 1223-1226 of the A loop bulge toward the N loop in an type II' β turn formation, with Leu-1225 at the apex of this turn. This Leucine forms a van der Waals interaction with Gly-1128. The K-252a shows a divergence from Apo-Met in residues 1228-1230. In the active confromation, Glu-1127 would form a salt bridge with Lys-1110, but in the K-252a complex, the A loop does not allow proper positioning of this residue, and so blocks nucleotide binding. Asp-1235 of the chain is interacting with the amide nitrogens of Ala-1243 and Ala-1244. There is also an interaction between Phe-1234 and Arg-1208 and Trp-1249. This conformation seems to be conserved in wild type c-met inhibited structures, and so is not causes by the mutations.
Some of the main conformational changes involve the A-loop, specifically residues 1228-1230. In the Apo-Met structure, the side chain of Met-1229 would pass through the six-membered ring of the indolocarbzole moiety. But, in this structure, because of the binding of K-252a, Met-1229 and Tyr-1230 move by 3.8 and 3.1 A. In order to make room for the side chain of Tyr-1230, arg-1208 moves by 8 A toward Asp-1204.[16]
C-Terminal Docking Site
There are two binding motifs of the docking site, 1356YVNV and 1349YVHV, each containing a tyrosine that gets phosphorylated. These tyrosines correspond to residues 1349 and 1356. In this strcuture, as mentioned above, these tyrosine residues have been subsituted for phenylalanines and so do not become phosphorylated. Because of this, residues 1349-1352 forma an extended confomatioin, while residues 1353-1356 and 1356-1359 form β turns. Both of these become phosphorylated, and act as docking sites for many signal transducers through interaction with their SH2, MBD and PTB domains. [17]
References
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C-Met
- ↑ Maina F, Casagranda F, Audero E, Simeone A, Comoglio PM, Klein R, Ponzetto C. Uncoupling of Grb2 from the Met receptor in vivo reveals complex roles in muscle development. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):531-42. PMID:8898205
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100