From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link Structural features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from an archaebacterium
Scheme
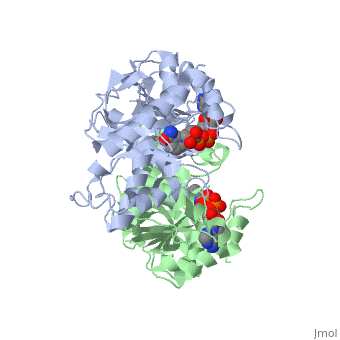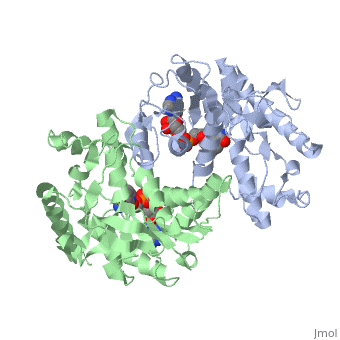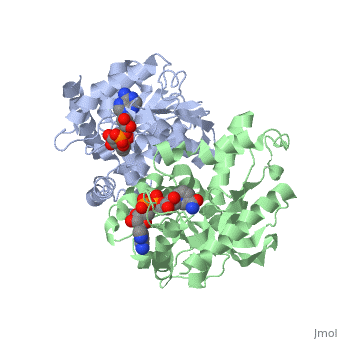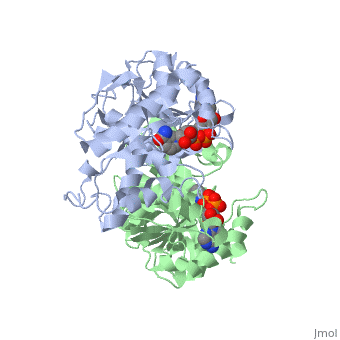
The high-resolution structure of halophilic malate dehydrogenase (hMDH) from the archaebacterium Haloarcula marismortui [[1]] was determined by x-ray crystallography. Comparison of the three-dimensional structures of hMDH and its nonhalophilic congeners reveals structural features that may promote the stability of hMDH at high salt concentrations. These features include an excess of acidic over basic residues distributed on the enzyme surface and more salt bridges present in hMDH compared with its nonhalophilic counterparts. Other features that contribute to the stabilization of thermophilic lactate dehydrogenase and thermophilic MDH-the incorporation of alanine into alpha helices and the introduction of negatively charged amino acids near their amino termini, both of which stabilize the alpha helix as a result of interaction with the positive part of the alpha-helix dipole-also were observed in hMDH