We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 714
From Proteopedia
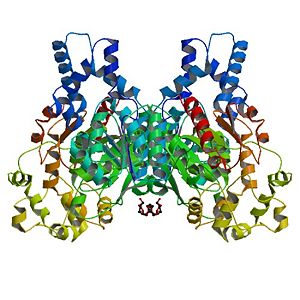
Human Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase: Biological assembly, 1s8o
Contents |
Overview
| |||||||||||
External ressources
References
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
DUTREUX Fabien, BONHOURE Anna

