From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
Introduction
Plectin is a multidomain protein with large size (>500kDa) and versatile binding properties, which abundantly expressed in a wide variety of mammalian tissues and cell types, combined with different binding partners. It has important functions in maintaining the mechanical stability of skin, skeletal muscle and heart.
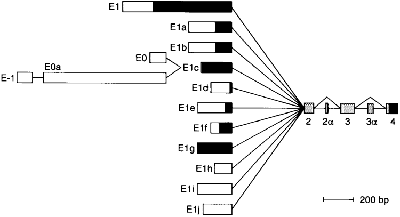
The plectin gene has unusual 5'-end diversity, which is alternatively spliced into exon 2 and makes 11 kinds of isoforms.
Expression level of isofroms is varied in tissues,and some of them are specifically expressed in brain,skeletal muscle and skin . [1].
Structures
Plectin can be divided in three main sections; a central coiled-coil rod domain, N and C-terminal globular region and exhibits a dumbbell like structure. C-terminal region is composed of 6 homologous repeating domains, and this region has a role in binding to intermediate filaments such as vimentin and cytokeratin [2]. N-terminal globular region contains actin binding domain (ABD) comprising two calponin homology.
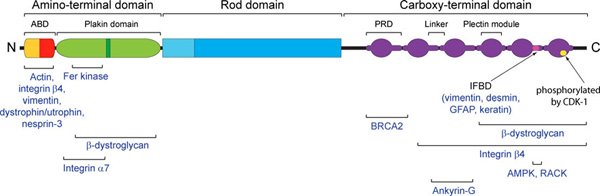
Schematic domain map of plectin (Winter, 2013)
1. Actin Binding Domain (ABD)
Plectin has a canonical actin binding domain in N-terminus, which is consisted of two calponin homology domain()[3]. N-terminal domain of plectin containing ABD interacts with F-actin and regulates actin dynamics in vivo, additionally binding of plectin ABD to vimentin was also reported [4].
2. Plakin domain
The plakin domain is formed by an array of spectrin repeats (SR) and a Src-homology 3 (SH3), and harbors binding sites for junctional proteins. This region is adjacent to the actin-binding domain and is required for efficient binding to the integrin alpha6beta4 in hemidesmosomes.[5]
3. Integrin β4-Plectin complex
The interaction between the integrin α6β4 and plectin is essential for the assembly and stability of hemidesmosomes, which are junctional adhesion complexes that anchor epithelial cells to the basement membrane.[6]
| TextToBeDisplayed</scene> />
Function and Interactions
Proteins coordinate various cytoskeletal networks are termed as cytolinkers, which are able to interlink different types of cytoskeletons. Plectin is one of the well-characterized cytolinker and expressed in diverse cell types and tissues, a number of different binding partners of plectin have been identified.
Intermediate filament(IF) binding sites of plectin is located between plakin repeats 5 and 6 in C-terminal globular domain. Several IF proteins were identified to interact with plectin such as vimentin, desmin, GFAP(glial fibrillary acidic protein) and cytokeratins [7] .
The actin binding domain(ABD)in N-terminal globular domain has a role to interact with integrin subunit beta 4 to establish mechanical stability in hemedesmosomes along with its function for binding to actin filament(F-actin). Calmodulin(CaM) is also known to bind the ABD of plectin to modulate the hemidesmosome disassembly [8].
Pathology
It has been reported that patients with EBS-MD (Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy),a genetic disorder characterized severe skin blistering disease combined with muscular dystrophy, have a muation on plectin gene(PLEC1). This mutation leads to premature termination of translation.[9]
In addition, site-specific missense mutation(R2110W) on plectin rod domain causes an autosomal dominant form of disease termed EBS-Ogna without muscular dystrophy.[10]
Plectin deficient(-/-) mice also exhibit similar skin and muscle phenotypes of human patients suffering from EBS-MD and died 2-3 days after birth. [11]
References
- ↑ Fuchs P, Zorer M, Rezniczek GA, Spazierer D, Oehler S, Castanon MJ, Hauptmann R, Wiche G. Unusual 5' transcript complexity of plectin isoforms: novel tissue-specific exons modulate actin binding activity. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Dec;8(13):2461-72. PMID:10556294
- ↑ Foisner R, Wiche G. Structure and hydrodynamic properties of plectin molecules. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):515-31. PMID:3430617
- ↑ Djinovic Carugo K, Banuelos S, Saraste M. Crystal structure of a calponin homology domain. Nat Struct Biol. 1997 Mar;4(3):175-9. PMID:9164454
- ↑ Sevcik J, Urbanikova L, Kost'an J, Janda L, Wiche G. Actin-binding domain of mouse plectin. Crystal structure and binding to vimentin. Eur J Biochem. 2004 May;271(10):1873-84. PMID:15128297 doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04095.x
- ↑ Ortega E, Buey RM, Sonnenberg A, de Pereda JM. The Structure of the Plakin Domain of Plectin Reveals a Non-canonical SH3 Domain Interacting with Its Fourth Spectrin Repeat. J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12429-38. Epub 2011 Feb 1. PMID:21288893 doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.197467
- ↑ de Pereda JM, Lillo MP, Sonnenberg A. Structural basis of the interaction between integrin alpha6beta4 and plectin at the hemidesmosomes. EMBO J. 2009 Apr 22;28(8):1180-90. Epub 2009 Feb 26. PMID:19242489 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.48
- ↑ Nikolic B, Mac Nulty E, Mir B, Wiche G. Basic amino acid residue cluster within nuclear targeting sequence motif is essential for cytoplasmic plectin-vimentin network junctions. J Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;134(6):1455-67. PMID:8830774
- ↑ Kostan J, Gregor M, Walko G, Wiche G. Plectin isoform-dependent regulation of keratin-integrin alpha6beta4 anchorage via Ca2+/calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 3;284(27):18525-36. Epub 2009 May 6. PMID:19419971 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.008474
- ↑ Chavanas S, Pulkkinen L, Gache Y, Smith FJ, McLean WH, Uitto J, Ortonne JP, Meneguzzi G. A homozygous nonsense mutation in the PLEC1 gene in patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1996 Nov 15;98(10):2196-200. PMID:8941634 doi:10.1172/JCI119028
- ↑ Koss-Harnes D, Jahnsen FL, Wiche G, Soyland E, Brandtzaeg P, Gedde-Dahl T Jr. Plectin abnormality in epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna: non-responsiveness of basal keratinocytes to some anti-rat plectin antibodies. Exp Dermatol. 1997 Feb;6(1):41-8. PMID:9067706
- ↑ Andra K, Lassmann H, Bittner R, Shorny S, Fassler R, Propst F, Wiche G. Targeted inactivation of plectin reveals essential function in maintaining the integrity of skin, muscle, and heart cytoarchitecture. Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 1;11(23):3143-56. PMID:9389647
|



