This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Single stranded binding protein
From Proteopedia
Contents |
Sandbox Single Stranded DNA-Binding Protein (SSB)
| |||||||||||
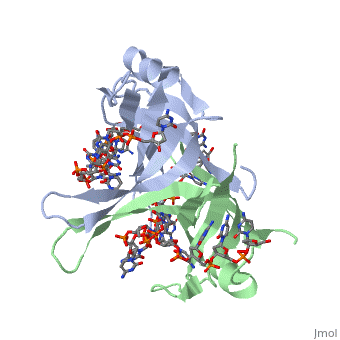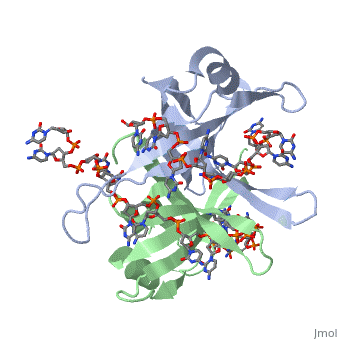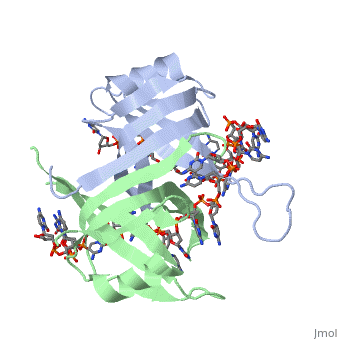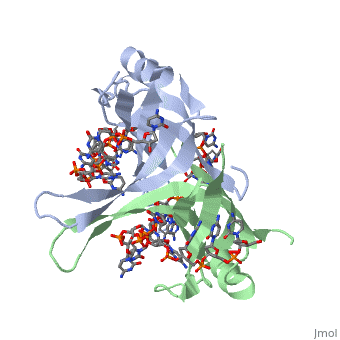
Binding Interactions in the Active Site
Phe-60 is an important DNA binding site. It has been shown to be the site for cross-linking.
Tryptophan and Lysine residues are important in binding as well. “Treatments resulting in
modification of arginine, cysteine, or tyrosine residues had no effect on binding of SSB to
DNA, whereas modification of either lysine residues (with acetic anhydride) or tryptophan
residues (with N-bromosuccinimide) led to complete loss of binding activity” ( Meyer, 348). The two tryptophan residues involved in DNA binding are Try-40 and Try-54, which was determined by mutagenesis. One more binding site was determined by site-specific mutagenesis.
When His-55 is substituted with Leu it decreases binding affinity. All of these residues
are found in a hydrophobic region, which is suitable for nucleotide base interactions.
SSB-Protein Interactions
It is believed that Gly-15 may play an important role in binding the RecA protein. Mutations in Gly-15 have extreme effects on recombinational repair. SSB has also been thought to bind with exonuclease I, DNA polymerase II, and a protein n, which is used to help synthesize RNA primers for the lagging strand.
| |||||||||||
See Also
References
PMID: 2087220
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Refayat Ahsen, Rachel Craig, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky