Sandbox Reserved 764
From Proteopedia
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Sep 25, 2013, through Mar 31, 2014 for use in the course "BCH455/555 Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Michael B. Goshe at the North Carolina State University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 299, Sandbox Reserved 300 and Sandbox Reserved 760 through Sandbox Reserved 779. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
|
Contents |
5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase
Formula weight:
Classification: transferase
Length: residues
Chains: A,B,C,D
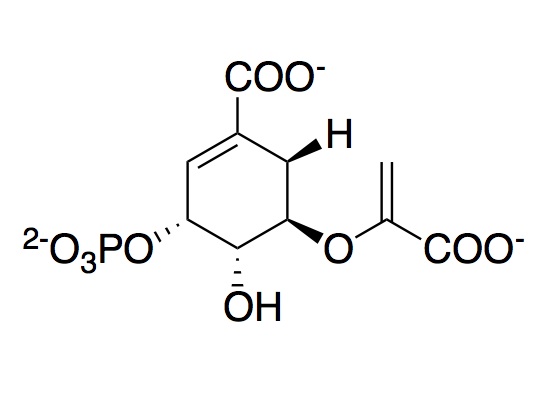
The monomeric enzyme 5-Enolpyruvlyshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) is an enzyme involved in the shikimate pathway found only in plants and microorganisms. The shikimate pathway is essential for the biosynthesis of chorismate, which is the precursor for aromatic amino acids and secondary aromatic metabolites. EPSP synthase uses phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to covert shikimate-3-phosphate (S3P) to 5-enolpyruvyl-3-shikimate phosphate, a precursor to majority of the aromatic compounds produced in the cell, including the aromatic amino acids (L-tyrosine, L-phenylalanine, L-tryptophan) that are needed for protein synthesis.
EPSP Synthase Structure
EPSP Synthase Mechanism
Implicatons
The implications in studying EPSP synthase involve the fact that this enzyme is not present in humans but is essential for bacteria and apicomplexan parasites. This makes EPSP synthase a selective target for antimicrobial drugs and decreases possible negative impacts of drugs in humans.