Anthrax Lethal Factor
From Proteopedia
Introduction
Anthrax Lethal Factor (LF) is one of the enzymatic components belonging to the Anthrax Toxin. Anthrax toxin is a three component exotoxin secreted by the bacterium Bacillus Anthracis made up of a binding protein, protective antigen (PA) and two enzyme components edema factor (EF) and lethal factor (LF). [1]
Anthrax Toxin, encoded by plasmid pXO1, is considered an AB toxin, with two A domains (EF and LF) and one B domain (PA). [1] [2] On their own, these three domains are nontoxic, but any combination involving PA with EF and/or LF is what causes the physiological effects. [3] Initially PA is a 83kDa protein which binds to the host Anthrax toxin Receptor (ATR). Upon binding, PA is cleaved into two fragments by furin proteases to become a 63 kDa protein bound to the ATR. Cleavage of PA allows self association to occur which forms a ring shaped heptamer know as the pore precursor (prepore). The prepore is now able to bind up to three molecules of EF and/or LF, leading to endocytosis of the complex. In the endosome, the prepore converts to a transmembrane pore, allowing translocation of EF and LF to the cytosol of target cell through a mechanism that is not well understood. EF and LF are now able to carry out their enzymatic activity on the host cell. [1]
EF is a calmodulin and calcium dependent adenylate cyclase that increases cAMP to extraordinary levels in cells. Changes in intracellular cAMP affect membrane permeability and may account for edema. In macrophages and neutrophils an additional effect is the depletion of ATP reserves which are needed for the engulfment process. [1] [4] [5]
LF is a Zinc dependent protease that cleaves certain MAP kinase kinases (MAPKK)leading to the disruption of many cellular signalling pathways, which eventually leads to cell death. [1] [6]
This is a list of the possible combinations that can occur with Anthrax Toxin: [7]
PA+LF Leads to lethal activity
EF+PA Leads to edema
EF+LF Non-toxic
PA+LF+EF Leads to lethal activity and edema
| |||||||||||
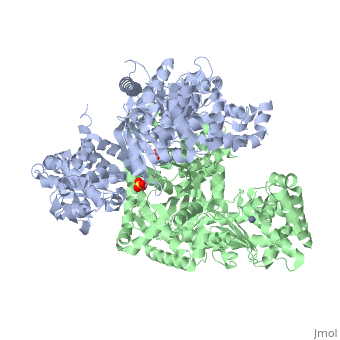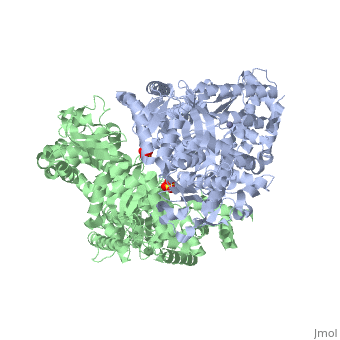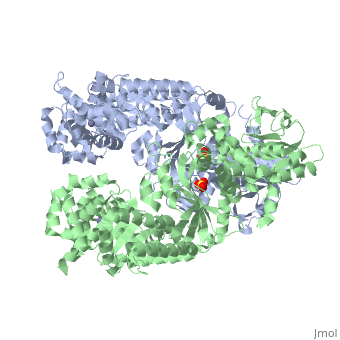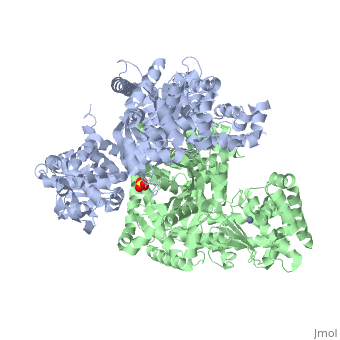
3D structures of anthrax lethal factor
Updated on 02-February-2014
1j7n – BaALF – Bacillus anthracis
2l0r – BaALF catalytic domain – NMR
1pwp, 1pwq, 1pwu, 1zxv, 4dv8 – BaALF + inhibitor
1yqy – BaALF domains II-IV + inhibitor
1pww, 1pwv – BaALF + peptide substrate
3kwv – BaALF protective antigen-binding domain + protective antigen
1yqy – BaALF domain IV - NMR
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 Collier RJ, Young JA. Anthrax toxin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:45-70. PMID:14570563 doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.140655
- ↑ Brenda A. Wilson, Abigail A. Salyers, Dixie D. Whitt, and Malcolm E. Winkler. Third Edition. Bacterial Pathogenesis A Molecular Approach
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html
- ↑ CDC. http://www.bt.cdc.gov/agent/anthrax/faq/treatment.asp
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R, Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S, Leppla SH, Hanna P, Liddington RC. Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor. Nature. 2001 Nov 8;414(6860):229-33. PMID:11700563 doi:10.1038/n35101998
- ↑ Moayeri M, Leppla SH. Cellular and systemic effects of anthrax lethal toxin and edema toxin. Mol Aspects Med. 2009 Dec;30(6):439-55. Epub 2009 Jul 26. PMID:19638283 doi:10.1016/j.mam.2009.07.003
- ↑ Brenda A. Wilson, Abigail A. Salyers, Dixie D. Whitt, and Malcolm E. Winkler. Third Edition. Bacterial Pathogenesis A Molecular Approach
- ↑ Brenda A. Wilson, Abigail A. Salyers, Dixie D. Whitt, and Malcolm E. Winkler. Third Edition. Bacterial Pathogenesis A Molecular Approach
- ↑ Kenneth Todar, PhD. (2008). http://textbookofbacteriology.net/Anthrax_3.html