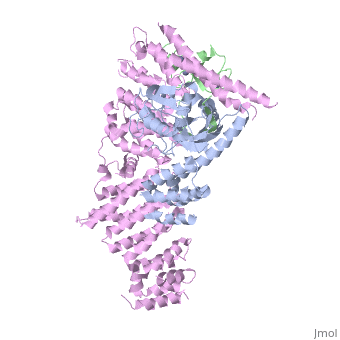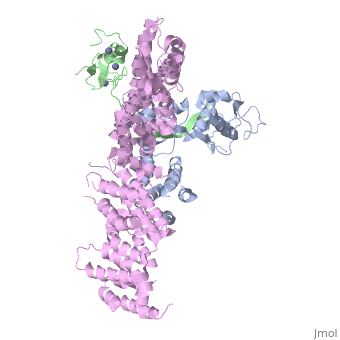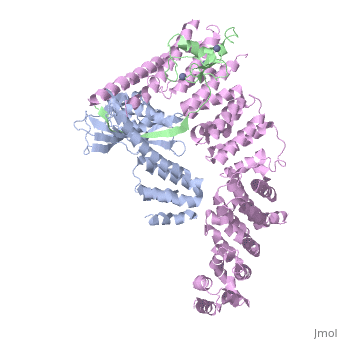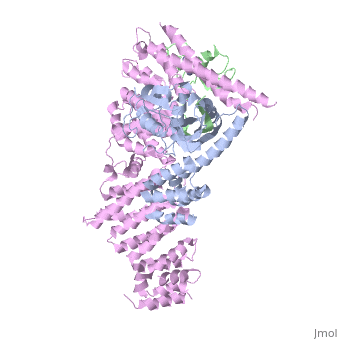| Structural highlights
4f52 is a 6 chain structure with sequence from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
| | Ligands: |
| | Gene: | CUL1 (Homo sapiens), RBX1, RNF75, ROC1 (Homo sapiens), GLMN, FAP48, FAP68, VMGLOM (Homo sapiens) |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum |
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The approximately 300 human cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) are multisubunit E3s in which a RING protein, either RBX1 or RBX2, recruits an E2 to catalyze ubiquitination. RBX1-containing CRLs also can bind Glomulin (GLMN), which binds RBX1's RING domain, regulates the RBX1-CUL1-containing SCF(FBW7) complex, and is disrupted in the disease Glomuvenous Malformation. Here we report the crystal structure of a complex between GLMN, RBX1, and a fragment of CUL1. Structural and biochemical analyses reveal that GLMN adopts a HEAT-like repeat fold that tightly binds the E2-interacting surface of RBX1, inhibiting CRL-mediated chain formation by the E2 CDC34. The structure explains the basis for GLMN's selectivity toward RBX1 over RBX2, and how disease-associated mutations disrupt GLMN-RBX1 interactions. Our study reveals a mechanism for RING E3 ligase regulation, whereby an inhibitor blocks E2 access, and raises the possibility that other E3s are likewise controlled by cellular proteins that mask E2-binding surfaces to mediate inhibition.
Structure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 Complex: Inhibition of a RING E3 Ligase through Masking of Its E2-Binding Surface.,Duda DM, Olszewski JL, Tron AE, Hammel M, Lambert LJ, Waddell MB, Mittag T, Decaprio JA, Schulman BA Mol Cell. 2012 Aug 10;47(3):371-82. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PMID:22748924[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Duda DM, Olszewski JL, Tron AE, Hammel M, Lambert LJ, Waddell MB, Mittag T, Decaprio JA, Schulman BA. Structure of a Glomulin-RBX1-CUL1 Complex: Inhibition of a RING E3 Ligase through Masking of Its E2-Binding Surface. Mol Cell. 2012 Aug 10;47(3):371-82. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PMID:22748924 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.044
|