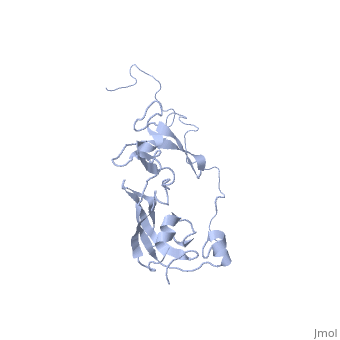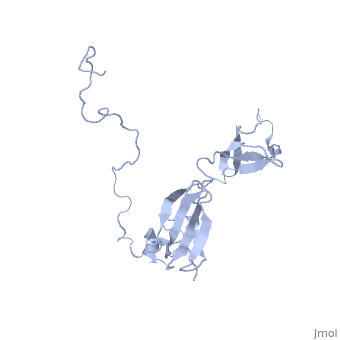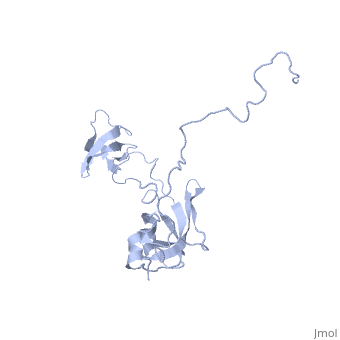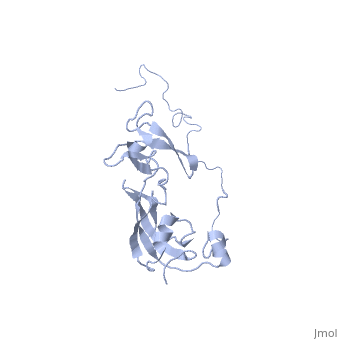This is a default text for your page The Escherichia coli sensitive to lysis D (SlyD) protein. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function
is a member of the FKBP family, it harbours prolyl isomerase activity, which is responsible for accelerating the rate-limiting trans-to-cis isomerization step in protein folding.
Structural highlights
In solution, SlyD folds into two globular domains, namely the and the , bisected by a deep . The PPIase domain of SlyD possesses a topology, and folds to generate a twisted four-stranded antiparallel b-sheet wrapped around the a1-helix and flanked by the a4-helix. The IF domain of SlyD displays a b6–a3–b9–b8–b7 topology, and folds to generate a four-stranded antiparallel b-sheet bordered by a short a3-helix
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
Disease
Relevance