Structural highlights
Function
[TAT_EIAVY] Nuclear transcriptional activator of viral gene expression, that is essential for viral transcription from the LTR promoter and replication. Acts as a sequence-specific molecular adapter, directing components of the cellular transcription machinery to the viral RNA to enhance transcription by the RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) complex, thereby increasing the level of full-length transcripts. Tat associates with the CCNT1/cyclin-T1 component of the P-TEFb complex (CDK9 and CCNT1), which promotes RNA chain elongation. This binding increases Tat's affinity for a branched hairpin structure at the 5'-end of all nascent viral mRNAs referred to as the transactivation responsive RNA element (TAR RNA). The CDK9 component of P-TEFb hyperphosphorylates the C-terminus of RNA Pol II that becomes stabilized and much more processive (Probable).
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
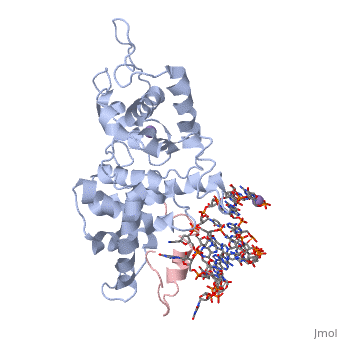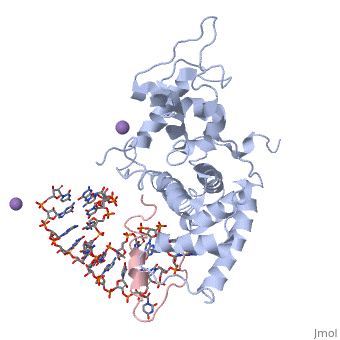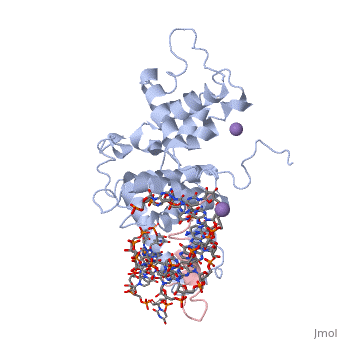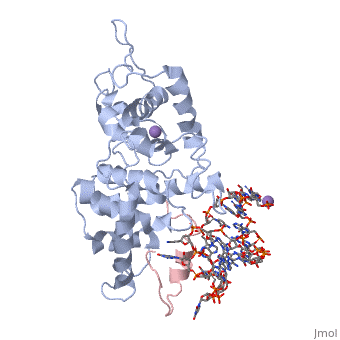
The replication of many retroviruses is mediated by a transcriptional activator protein, Tat, which activates RNA polymerase II at the level of transcription elongation. Tat interacts with Cyclin T1 of the positive transcription-elongation factor P-TEFb to recruit the transactivation-response TAR RNA, which acts as a promoter element in the transcribed 5' end of the viral long terminal repeat. Here we present the structure of the cyclin box domain of Cyclin T1 in complex with the Tat protein from the equine infectious anemia virus and its corresponding TAR RNA. The basic RNA-recognition motif of Tat adopts a helical structure whose flanking regions interact with a cyclin T-specific loop in the first cyclin box repeat. Together, both proteins coordinate the stem-loop structure of TAR. Our findings show that Tat binds to a surface on Cyclin T1 similar to where recognition motifs from substrate and inhibitor peptides were previously found to interact within Cdk-cyclin pairs.
Structural insights into the cyclin T1-Tat-TAR RNA transcription activation complex from EIAV.,Anand K, Schulte A, Vogel-Bachmayr K, Scheffzek K, Geyer M Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Dec;15(12):1287-92. Epub 2008 Nov 23. PMID:19029897[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Anand K, Schulte A, Vogel-Bachmayr K, Scheffzek K, Geyer M. Structural insights into the cyclin T1-Tat-TAR RNA transcription activation complex from EIAV. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Dec;15(12):1287-92. Epub 2008 Nov 23. PMID:19029897 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1513