UBC13 MMS2
From Proteopedia
6. Moraes, T. F.; FAU, E. R.; McKenna, S. F.; Pastushok, L. F.; Xiao W FAU - Glover,,J.N.; FAU, G. J.; Ellison, M. J. Crystal structure of the human ubiquitin conjugating enzyme complex, hMms2-hUbc13. Nature structural biology JID - 9421566 0816.</ref> ' scene='69/695700/Ubc13_mms2_overall/1' />
SummaryUbc13 is an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that can form a heterodimer with Mms2 to function as a part of the translesion synthesis (TLS) pathway,[1][2]. When bound to Mms2, Ubc13 will polyubiquitinate proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), a sliding clamp protein at the DNA transcription fork[1]. Ubc13-Mms2 functions to polyubiquitinate PCNA following the initial monoubiquitination by Rad6-Rad18 (another E2 complex)[2]. FunctionUbc13 functions as a heterodimer with Mms2, a structurally similar protein to Ubc13 that lacks the catalytic cysteine residue in the active site[3][4]. The Ubc13-E2 complex with Mms2 functions primarily to enhance DNA repair from double stranded breaks. Mms2 bound to Ubc13 helps orient the ubiquitin molecule for proper ubiquitination of the K63 residue. Mms2 is considered a Ubiquitin E2 variant (UEV) protein, because it lacks the catalytic cysteine residue necessary for proper thioester formation[3]. RegulationThe regulation of Ubc13 is controlled by the competitive binding of the two different UEV's, Mms2 and UEV1A[2]. Ubc13 binding to Mms2 activates the DNA repair pathway, while Ubc13 binding to UEV1A activates the NF-kappaB pathway, a gene regulation pathway involved in DNA transcription factors[2]. These two opposing pathways being downstream targets for Ubc13-bound complexes is the basis for regulation. Coordinating Enzymes
Pathway for DNA Repair
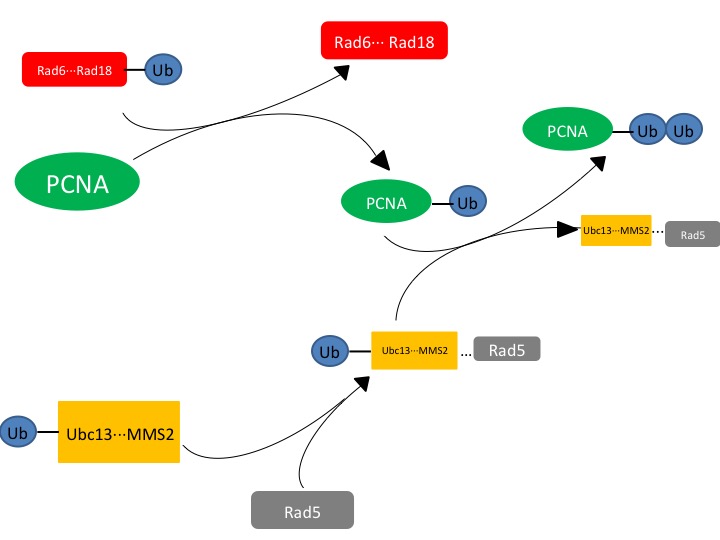
Figure. 1. The affected protein PCNA is a DNA clamp that is monoubiquitinated by the Rad6-Rad18 complex. The monoubiquitinated PCNA is then polyubuiquitinated by the UBC13-Mms2-Rad5 complex.
Structural Highlights/Important ResiduesUbc13 weights 17.6 kDA, and Mms2 is 16.8 kDA[4]. The heterodimer is stable at high stalt concentrations (1 M), suggesting strong interactions between the two. Kd between the Ubc13 and Mms2 is 2 uM. Phe57 and Glu55 of Ubc13 interact with the N-terminal domain of Mms2 to ensure stable docking[4]. Additionally, Arg70 hydrophobically interacts with an alpha helix of Mms2 in two places[4]. Mms2’s Phe13 is inserted between Glu55, Phe57, and Arg70 of Ubc13 to create a hydrophobic pocket[4]. It is therorized that Glu55 and Arg70 of Ubc13 are more important for recognition instead of stability[4]. MechanismThe exact mechanism for how Ubc13 transfers ubiquitin is not known, however the mechanism occurs in either a step-wise or concerted reaction.
References
| ||||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David A Taves, Michal Harel, Christopher Alexander Hudson, Nicholas R. Dunham