Introduction
This scene is of the within the Kappa Opioid Receptor by Group 3.
-"Kappa-Opioid receptors mediate the regulation of pain, respiratory drive, mood"
-"structure reveals important features of the ligand-binding pocket that contribute to the high affinity and subtype selectivity of JDTic for the human kappa-OR"
-consequences of stress as well as depression/anxiety
-hallucinogenic effects
-talk about mu and kappa OR
-intro to kappa-OR subtype selectivity
Overall Structure
Copy and paste the following line where you want the scene link to appear (scroll down if needed) and edit the TextToBeDisplayed:
-describe the overall size of the molecule: how massive it is, how many alpha helices and beta sheets it contains.
-describe the two different dimmers that form the protien and how and along which alpha helices the dimmers coordinate with each other
-describe how the protein fits in the cell membrane, how much is contained in the membrane.
-describe which parts are conserved and which parts make it a unique molecule like how the sulfide bond near the n-terminus among other feature distinguishes itself from CXCR4
-describe the structure and shape of the binding pocket, discuss how these structural conformations make it unique.
Binding Interactions
Active Site of kappa Opioid Receptors
Common Ligands of Opioid Receptors
Agonists Salvinorin A - Mechanisms, Structure, and Effects
Antagonists JDTic - Mechanisms, Structure, and Effects
Additional Features
The k-opioid receptor is a protein, with inter-membrane alpha helices displayed in red.

A hydropathy plot for this receptor reinforces this fact, with a large span of the molecule shown again as trans-membrane alpha helices.
Based on the Ramachandran plot for the general case showing the standard phi and psi angle, it can be inferred that the majority of the secondary structure is composed , with the alpha helices shown in purple and the beta sheets shown in yellow.
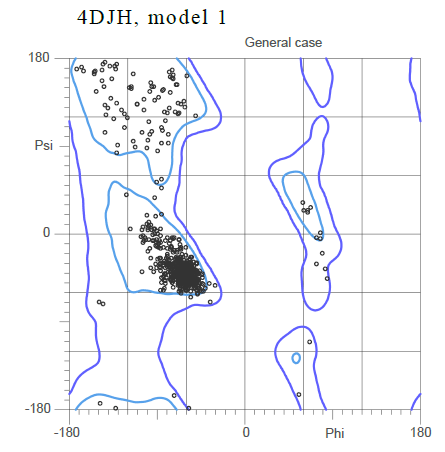
The large cluster of dots shown close to the origin of the plot corresponds to small angles that imply an alpha helix.
Quiz Question 1
Why might the , highlighted in blue, be located here in the protein? (Explain how its location and other properties of the protein maintain binding specificity.) What basic conformational changes may the protein undergo while binding to ligands?
Quiz Question 2
What properties and functional groups would a substrate binding to the active site of the Kappa-opioid receptor probably possess? Explain your reasoning.
See Also
Credits
Introduction - Patrick Harney
Overall Structure - Matthew Long
Drug Binding Site - Brandon Kittredge
Additional Features - Jacob Kellet
Quiz Question 1 - Leah Caffrey
Quiz Question 2 - Bridget Kilkenny
References
1. Chavkin C., The Therapeutic Potential of κ-Opioids for Treatment of Pain and Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:369–370.
2. Wu H., Wacker D., Mileni M., Structure of the human kappa opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature. 2012;485:327-332. PMID:22437504
3. Martinez-Mayorga K., Byler K., Yongye A., et al. Ligand/kappa-opioid Receptor Ineractions: Insights from the X-Ray Crystal Structure. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2013; 66: 114-121.

